Stereological Analysis of Early Gene Expression Using Egr-1 Immunolabeling After Spreading Depression in the Rat Somatosensory Cortex
- PMID: 31607855
- PMCID: PMC6774394
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01020
Stereological Analysis of Early Gene Expression Using Egr-1 Immunolabeling After Spreading Depression in the Rat Somatosensory Cortex
Abstract
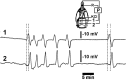
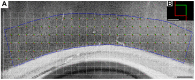
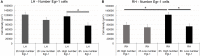
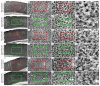
Early growth response-1 (Egr-1), defined as a zinc finger transcription factor, is an upstream master switch of the inflammatory response, and its expression can be used to investigate the spatial and temporal extent of inflammatory changes in the brain. Cortical spreading depression (CSD) is characterized as a slowly propagating (2-5 mm/min) depolarization wave through neurons and astrocytes in humans that contributes to migraines and possibly to other brain pathologies. In rodents, CSD can be induced experimentally, which involves unilateral depolarization that is associated with microglial and astrocyte responses. The impact of CSD on structures beyond the affected hemisphere has not been explored. Here, we used an optical fractionator method to investigate potential correlations between the number of and period of the eletrophysiologic record of CSD phenomena and Egr-1 expression in ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres. CSD was elicited by the restricted application of a 2% KCl solution over the left premotor cortex. Electrophysiological events were recorded using a pair of Ag/AgCl agar-Ringer electrodes for 2 or 6 h. An optical fractionator was applied to count the Egr-1 positive cells. We found that CSD increased Egr-1 expression in a time- and event-dependent manner in the ipsilateral/left hemisphere. Although CSD did not cross the midline, multiple CSD inductions were associated with an increased number of Egr-1 positive cells in the contralateral/right hemisphere. Thus, repeated CSD waves may have far reaching effects that are more global than previously considered possible. The mechanism of contralateral expression is unknown, but we speculate that callosal projections from the depolarized hemisphere may be related to this phenomenon.
Keywords: Egr-1; contralateral hemisphere; cortical spreading depression; optical fractionator; somatosensorial cortex.
Copyright © 2019 Sosthenes, Diniz, Roodselaar, Abadie-Guedes, Siqueira Mendes, Fernandes, Bittencourt, Diniz, Anthony and Guedes.
Figures




References
-
- Bento-Torres J., Sobral L. L., Reis R. R., de Oliveira R. B., Anthony D. C., Vasconcelos P. F., et al. (2017). Age and environment influences on mouse prion disease progression: behavioral changes and morphometry and stereology of hippocampal astrocytes. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017:4504925. 10.1155/2017/4504925 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

