Glutathione Can Compensate for Salicylic Acid Deficiency in Tobacco to Maintain Resistance to Tobacco Mosaic Virus
- PMID: 31608082
- PMCID: PMC6769422
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01115
Glutathione Can Compensate for Salicylic Acid Deficiency in Tobacco to Maintain Resistance to Tobacco Mosaic Virus
Abstract
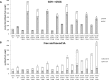
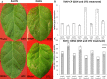
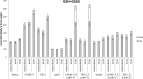
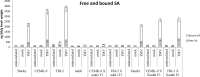
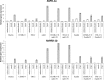
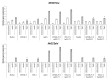
Earlier studies showed that the artificial elevation of endogenous glutathione (GSH) contents can markedly increase the resistance of plants against different viruses. On the other hand, salicylic acid (SA)-deficient NahG plants display enhanced susceptibility to viral infections. In the present study, the biochemical mechanisms underlying GSH-induced resistance were investigated in various tobacco biotypes displaying markedly different GSH and SA levels. The endogenous GSH levels of Nicotiana tabacum cv. Xanthi NN and N. tabacum cv. Xanthi NN NahG tobacco leaves were increased by infiltration of exogenous GSH or its synthetic precursor R-2-oxo-4-thiazolidine-carboxylic acid (OTC). Alternatively, we also used tobacco lines containing high GSH levels due to transgenes encoding critical enzymes for cysteine and GSH biosynthesis. We crossed Xanthi NN and NahG tobaccos with the GSH overproducer transgenic tobacco lines in order to obtain F1 progenies with increased levels of GSH and decreased levels of SA. We demonstrated that in SA-deficient NahG tobacco the elevation of in planta GSH and GSSG levels either by exogenous GSH or by crossing with glutathione overproducing plants confers enhanced resistance to Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) manifested as both reduced symptoms (i.e. suppression of hypersensitive-type localized necrosis) and lower virus titers. The beneficial effects of elevated GSH on TMV resistance was markedly stronger in NahG than in Xanthi NN leaves. Infiltration of exogenous GSH and OTC or crossing with GSH overproducer tobacco lines resulted in a substantial rise of bound SA and to a lesser extent of free SA levels in tobacco, especially following TMV infection. Significant increases in expression of pathogenesis related (NtPR-1a, and NtPRB-1b), and glutathione S-transferase (NtGSTtau, and NtGSTphi) genes were evident in TMV-inoculated leaves in later stages of pathogenesis. However, the highest levels of defense gene expression were associated with SA-deficiency, rather than enhanced TMV resistance. In summary, elevated levels of glutathione in TMV-infected tobacco can compensate for SA deficiency to maintain virus resistance. Our results suggest that glutathione-induced redox changes are important components of antiviral signaling in tobacco.
Keywords: NahG; Tobacco mosaic virus; glutathione; salicylic acid; tobacco; virus resistance.
Copyright © 2019 Künstler, Király, Kátay, Enyedi and Gullner.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

