Techniques for Formulation of Nanoemulsion Drug Delivery System: A Review
- PMID: 31608247
- PMCID: PMC6779084
- DOI: 10.3746/pnf.2019.24.3.225
Techniques for Formulation of Nanoemulsion Drug Delivery System: A Review
Abstract
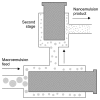
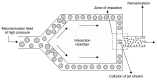
Nanoemulsion drug delivery systems are advanced modes for delivering and improving the bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs and the drug which have high first pass metabolism. The nanoemulsion can be prepared by both high energy and low energy methods. High energy method includes high-pressure homogenization, microfluidization, and ultrasonication whereas low energy methods include the phase inversion emulsification method and the self-nanoemulsification method. Low energy methods should be preferred over high energy methods as these methods require less energy, so are more efficient and do not require any sophisticated instruments. However high energy methods are more favorable for food grade emulsion as they require lower quantities of surfactant than low energy methods. Techniques for formulation of nanoemulsion drug delivery system are overlapping in nature, especially in the case of low energy methods. In this review, we have classified different methods for formulation of nanoemulsion systems based on energy requirements, nature of phase inversion, and self-emulsification.
Keywords: drug delivery; high energy method; low energy method; nanoemulsion; phase inversion methods.
Copyright © 2019 by The Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
AUTHOR DISCLOSURE STATEMENT The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Acosta E. Bioavailability of nanoparticles in nutrient and nutraceutical delivery. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci. 2009;14:3–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2008.01.002. - DOI
-
- Agrawal S, Giri TK, Tripathi DK, Ajazuddin Alexander A. A review on novel therapeutic strategies for the enhancement of solubility for hydrophobic drugs through lipid and surfactant based self micro emulsifying drug delivery system: a novel approach. Am J Drug Discovery Dev. 2012;2:143–183. doi: 10.3923/ajdd.2012.143.183. - DOI
-
- Akbas E, Soyler B, Oztop MH. Formation of capsaicin loaded nanoemulsions with high pressure homogenization and ultrasonication. LWT. 2018;96:266–273. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.05.043. - DOI
-
- Alshamsan A, Kazi M, Badran MM, Alanazi FK. Role of alternative lipid excipients in the design of self-nanoemulsifying formulations for fenofibrate: characterization, in vitro dispersion, digestion and ex vivo gut permeation studies. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1219. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01219. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armanet L, Hunkeler D. Phase inversion of polyacrylamide-based inverse-emulsions: influence of inverting-surfactant type and concentration. J Appl Polym Sci. 2007;103:3567–3584. doi: 10.1002/app.25062. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
