Measurement of plasma and platelet tissue factor pathway inhibitor, factor V and Protein S in people with haemophilia
- PMID: 31608540
- PMCID: PMC6995352
- DOI: 10.1111/hae.13860
Measurement of plasma and platelet tissue factor pathway inhibitor, factor V and Protein S in people with haemophilia
Abstract
Introduction: Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) is a naturally occurring anticoagulant found in plasma, where it circulates bound to lipoproteins, factor V (FV) or Protein S (PS), and in platelets. Therapeutic agents targeting TFPI are under development for the treatment of haemophilia A and haemophilia B.
Aim: To begin to understand how TFPI, FV and PS interact to modulate haemophilia bleeding.
Methods: Plasma and platelet antigen concentrations of these factors were determined in 73 people with haemophilia A and 18 with haemophilia B. Using multiple regression models, these were compared to the same analytes measured in 224 male blood donors.
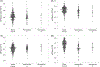
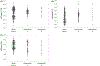
Results: There were no differences in plasma or platelet TFPI, FV or PS concentrations between haemophilia types or severities. However, compared to blood donors, people with haemophilia had approximately one-third lower plasma PS, 9% lower plasma TFPIα, 50% higher platelet FV and 26% lower platelet Protein S.
Conclusion: Together, the presented data suggest that individuals with haemophilia may have a compensatory procoagulant response of both plasma and platelet proteins to the decreased concentrations of FVIII or FIX.
Keywords: Protein S; factor V; haemophilia; tissue factor pathway inhibitor.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Rosendaal FR, Briet E. The increasing prevalence of haemophilia. Thromb Haemost. 1990;63(1):145. - PubMed
-
- Soucie JM, Evatt B, Jackson D. Occurrence of hemophilia in the United States. The hemophilia surveillance system project investigators. Am J Hematol. 1998;59(4):288–294. - PubMed
-
- Collins PW, Hirsch S, Baglin TP, et al. Acquired hemophilia A in the United Kingdom: a 2-year national surveillance study by the United Kingdom Haemophilia Centre Doctors’ Organisation. Blood. 2007;109(5):1870–1877. - PubMed
-
- Weyand AC, Pipe SW. New therapies for hemophilia. Blood. 2019;133(5):389–398. - PubMed
-
- Kulkarni R, Aledort LM, Berntorp E, et al. Therapeutic choices for patients with hemophilia and high-titer inhibitors. Am J Hematol. 2001;67(4):240–246. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

