A novel intraperitoneal therapy for gastric cancer with DFP-10825, a unique RNAi therapeutic targeting thymidylate synthase, in a peritoneally disseminated xenograft model
- PMID: 31609087
- PMCID: PMC6885878
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2598
A novel intraperitoneal therapy for gastric cancer with DFP-10825, a unique RNAi therapeutic targeting thymidylate synthase, in a peritoneally disseminated xenograft model
Abstract
Purpose: In advanced gastric cancer, peritoneal dissemination is a life-threatening mode of metastasis. Since the treatment options with conventional chemotherapy remain limited, any novel therapeutic strategy that could control such metastasis would improve the outcome of treatment. We recently developed a unique RNA interference therapeutic regimen (DFP-10825) consisting of short hairpin RNA against thymidylate synthase (TS shRNA) and cationic liposomes. The treatment with DFP-10825 has shown remarkable antitumor activity in peritoneally disseminated human ovarian cancer-bearing mice via intraperitoneal administration. In this study, we expanded DFP-10825 to the treatment of peritoneally disseminated gastric cancer.
Methods: DFP-10825 was administered intraperitoneally into mice with intraperitoneally implanted human gastric cancer cells (MKN45 or NCI-N87). Antitumor activity and host survival benefits were monitored. Intraperitoneal distribution of fluorescence-labeled DFP-10825 was monitored in this MKN45 peritoneally disseminated mouse model.
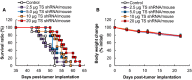
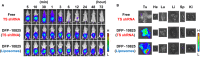
Results: Intraperitoneal injection of DFP-10825 suppressed tumor growth in two peritoneally disseminated cancer models (MKN45 and NCI-N87) and increased the survival time of the MKN45 model without severe side effects. Throughout the treatment regimen, no significant body weight loss was associated with the administration of DFP-10825. Interestingly, after intraperitoneal injection, fluorescence-labeled DFP-10825 retained for more than 72 hours in the peritoneal cavity and selectively accumulated in disseminated tumors.
Conclusions: Intraperitoneal injection of DFP-10825 demonstrated effective antitumor activity without systemic severe adverse effects via the selective delivery of RNAi molecules into disseminated tumors in the peritoneal cavity. Our current study indicates that DFP-10825 could become an alternative option to improve the outcomes of patients with peritoneally disseminated gastric cancer.
Keywords: DFP-10825; RNAi therapeutic; S-1; gastric cancer; peritoneal dissemination; thymidylate synthase (TS).
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
MF and KE are employees of Delta‐Fly Pharma, Inc. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anticancer activity of the intraperitoneal-delivered DFP-10825, the cationic liposome-conjugated RNAi molecule targeting thymidylate synthase, on peritoneal disseminated ovarian cancer xenograft model.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Mar 29;12:673-683. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S156635. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 29636601 Free PMC article.
-
An RNAi therapeutic, DFP-10825, for intraperitoneal and intrapleural malignant cancers.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;154-155:27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.08.002. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020. PMID: 32781056 Review.
-
I.p.-injected cationic liposomes are retained and accumulate in peritoneally disseminated tumors.J Control Release. 2022 Jan;341:524-532. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.12.004. Epub 2021 Dec 10. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 34896447
-
Therapeutic efficacy of a paclitaxel-loaded nanofibrillated bacterial cellulose (PTX/NFBC) formulation in a peritoneally disseminated gastric cancer xenograft model.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Mar 31;174:494-501. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.201. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33545180
-
Intraperitoneal chemotherapy for gastric cancer with peritoneal disease: experience from Singapore and Japan.Gastric Cancer. 2017 Mar;20(Suppl 1):122-127. doi: 10.1007/s10120-016-0660-y. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Gastric Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27766496 Review.
Cited by
-
Intraperitoneal Irrigation Chemotherapy with Lobaplatin in Locally Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Special Type of Abdominal Chemotherapy.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Jul 1;25(7):2409-2413. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.7.2409. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39068574 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in nucleic acid therapeutics: structures, delivery systems, and future perspectives in cancer treatment.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Aug 28;24(1):200. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01463-4. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39196428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping the intellectual structure and emerging trends for the application of nanomaterials in gastric cancer: A bibliometric study.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 May 15;16(5):2181-2199. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2181. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38764848 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging therapeutic approaches for peritoneal metastases from gastrointestinal cancers.Mol Ther Oncol. 2024 Jan 29;32(1):200767. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200767. eCollection 2024 Mar 21. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38596287 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359‐E386. - PubMed
-
- Sadeghi B, Arvieux C, Glehen O, et al. Peritoneal carcinomatosis from non‐gynecologic malignancies: results of the EVOCAPE 1 multicentric prospective study. Cancer. 2000;88:358‐363. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi I, Matsusaka T, Onohara T, et al. Clinicopathological features of long‐term survivors of scirrhous gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000;47:1485‐1488. - PubMed
-
- Jacquet P, Sugarbaker PH. Peritoneal‐plasma barrier. Cancer Treat Res. 1996;82:53‐63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

