β-blockers augment L-type Ca2+ channel activity by targeting spatially restricted β2AR signaling in neurons
- PMID: 31609201
- PMCID: PMC6813027
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.49464
β-blockers augment L-type Ca2+ channel activity by targeting spatially restricted β2AR signaling in neurons
Abstract
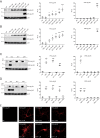
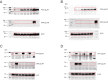
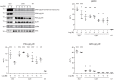
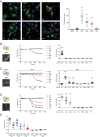
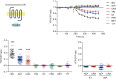
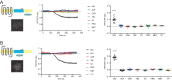
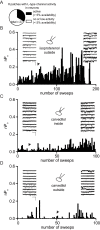
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) transduce pleiotropic intracellular signals in mammalian cells. Here, we report neuronal excitability of β-blockers carvedilol and alprenolol at clinically relevant nanomolar concentrations. Carvedilol and alprenolol activate β2AR, which promote G protein signaling and cAMP/PKA activities without action of G protein receptor kinases (GRKs). The cAMP/PKA activities are restricted within the immediate vicinity of activated β2AR, leading to selectively enhance PKA-dependent phosphorylation and stimulation of endogenous L-type calcium channel (LTCC) but not AMPA receptor in rat hippocampal neurons. Moreover, we have engineered a mutant β2AR that lacks the catecholamine binding pocket. This mutant is preferentially activated by carvedilol but not the orthosteric agonist isoproterenol. Carvedilol activates the mutant β2AR in mouse hippocampal neurons augmenting LTCC activity through cAMP/PKA signaling. Together, our study identifies a mechanism by which β-blocker-dependent activation of GPCRs promotes spatially restricted cAMP/PKA signaling to selectively target membrane downstream effectors such as LTCC in neurons.
Keywords: cell biology; hippocampus; ion channel; mouse; rat; signaling transduction.
© 2019, Shen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AS, DC, MK, PB, BX, QS, JM, KM, MN, JH, MN, XY, YX No competing interests declared
Figures


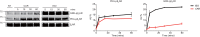




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL098200/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 129376/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- GM129376/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG055357/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Postdoctoral fellowship/American Heart Association/International
- HL121059/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002900/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- HL149127/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL098200/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM129376/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM099608/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- BX002900/U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs/International
- R01 HL149127/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121059/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

