A New Multimodel Machine Learning Framework to Improve Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Ultrasound Elastography Systems from Different Vendors
- PMID: 31611074
- PMCID: PMC6879839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.09.004
A New Multimodel Machine Learning Framework to Improve Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Ultrasound Elastography Systems from Different Vendors
Abstract
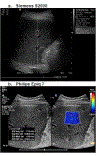
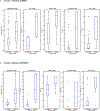
The purpose of the work described here was to determine if the diagnostic performance of point and 2-D shear wave elastography (pSWE; 2-DSWE) using shear wave velocity (SWV) with a new machine learning (ML) technique applied to systems from different vendors is comparable to that of magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) in distinguishing non-significant (<F2) from significant (≥F2) fibrosis. We included two patient groups with liver disease: (i) 144 patients undergoing pSWE (Siemens) and MRE; and (ii) 60 patients undergoing 2-DSWE (Philips) and MRE. Four ML algorithms using 10 SWV measurements as inputs were trained with MRE. Results were validated using twofold cross-validation. The performance of median SWV in binary grading of fibrosis was moderate for pSWE (area under the curve [AUC]: 0.76) and 2-DSWE (0.84); the ML algorithm support vector machine (SVM) performed particularly well (pSWE: 0.96, 2-DSWE: 0.99). The results suggest that the multivendor ML-based algorithm SVM can binarily grade liver fibrosis using ultrasound elastography with excellent diagnostic performance, comparable to that of MRE.
Keywords: Liver fibrosis; Machine learning; Shear wave elastography; Ultrasound.
Copyright © 2019 World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

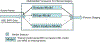
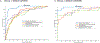
References
-
- Afdhal NH, Bacon BR, Patel K, Lawitz EJ, Gordon SC, Nelson DR, Challies TL, Nasser I, Garg J, Wei LJ, and McHutchison JG. ‘Accuracy of fibroscan, compared with histology, in analysis of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis B or C: a United States multicenter study’, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol,2015; 13: 772–9 e1–3. - PubMed
-
- Bota S, Sporea I, Sirli R, Popescu A, Danila M, and Costachescu D. ‘Intra- and interoperator reproducibility of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography--preliminary results’, Ultrasound Med Biol,2012; 38: 1103–8. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Luo Y, Huang W, Hu D, Zheng RQ, Cong SZ, Meng FK, Yang H, Lin HJ, Sun Y, Wang XY, Wu T, Ren J, Pei SF, Zheng Y, He Y, Hu Y, Yang N, and Yan H. ‘Machine-learning-based classification of real-time tissue elastography for hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B’, Comput Biol Med,2017; 89: 18–23. - PubMed
-
- Cui J, Heba E, Hernandez C, Haufe W, Hooker J, Andre MP, Valasek MA, Aryafar H, Sirlin CB, and Loomba R. ‘Magnetic resonance elastography is superior to acoustic radiation force impulse for the Diagnosis of fibrosis in patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective study’, Hepatology,2016; 63: 453–61. - PMC - PubMed
-
- D’Onofrio M, Gallotti A, and Mucelli RP. ‘Tissue quantification with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging: Measurement repeatability and normal values in the healthy liver’, AJR Am J Roentgenol,2010; 195: 132–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

