Susceptibility of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus to Five Quinazolinone Antibacterials
- PMID: 31611358
- PMCID: PMC7187613
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01344-19
Susceptibility of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus to Five Quinazolinone Antibacterials
Abstract
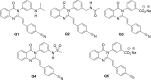
The in vitro activities of five quinazolinone antibacterials, compounds Q1 to Q5, were tested against 210 strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The MIC50/MIC90 values (in μg/ml) were as follows: Q1, 0.5/2; Q2, 1/4; Q3, 2/4; Q4, 0.06/0.25; and Q5, 0.125/0.5. Several strains with high MIC values (from 8 to >32 μg/ml) for some of these compounds exhibited amino acid changes in the penicillin-binding proteins, which are targeted by these antibacterials.
Keywords: MRSA; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; penicillin-binding proteins; quinazolinones; staphylococci.
Copyright © 2019 Ceballos et al.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2014. Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance. World Health Organization Press, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2013. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2013. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia.
-
- Testero SA, Fisher JF, Mobashery S. 2010. β-Lactam antibiotics, p 259–404. In Abraham DJ, Rotella DP (ed), Burger’s medicinal chemistry, drug discovery and development, vol 7 John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases