Pancreatic Cysts: Diagnostic Role of EUS-Guided Microforceps Biopsy and Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy
- PMID: 31611915
- PMCID: PMC6757287
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/3431048
Pancreatic Cysts: Diagnostic Role of EUS-Guided Microforceps Biopsy and Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy
Abstract
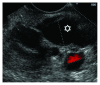
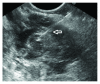
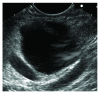
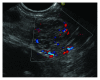
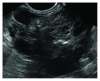
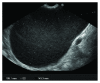
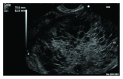
Frequent use of high-quality cross-sectional imaging has led to a significant rise in diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs). Despite the fact that enormous effort has been put into the research of PCLs within the last two decades and multiple guidelines have been developed, our clinical decision-making especially in regard to mucinous lesions remains limited. Currently, clinical assessment, cross-sectional imaging and EUS with fluid analysis (if appropriate) belong to the standard care in patients with PCLs. For differentiation of mucinous from nonmucinous cysts, the sensitivity of cytological investigation and CEA in the cyst fluid is 42% and 52-79%, respectively. Due to the limited accuracy, further diagnostic tools are warranted. Two EUS-guided approaches have been introduced recently. Through-the-(19-gauge EUS) needle Moray microforceps have been developed, and several studies have acknowledged their contribution to the correct diagnosis as they help to overcome limited cellularity of the EUS-guided cyst fluid aspiration and traditional cytology. Confocal laser endomicroscopy offers real-time images and seems to be a promising method for the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of pancreatic PCLs. Example images of the needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy criteria for the diagnosis of PCLs have been suggested recently. Before both, Moray microforceps and confocal laser endomicroscopy can be widely accepted, further studies are necessary to determine the real diagnostic yield and the clinical efficacy.
Copyright © 2019 Darina Kohoutova et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

