InGaN as a Substrate for AC Photoelectrochemical Imaging
- PMID: 31614420
- PMCID: PMC6832470
- DOI: 10.3390/s19204386
InGaN as a Substrate for AC Photoelectrochemical Imaging
Abstract
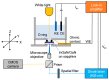
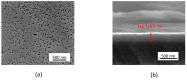
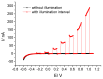
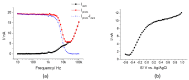
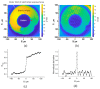
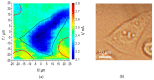
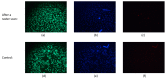
AC photoelectrochemical imaging at electrolyte-semiconductor interfaces provides spatially resolved information such as surface potentials, ion concentrations and electrical impedance. In this work, thin films of InGaN/GaN were used successfully for AC photoelectrochemical imaging, and experimentally shown to generate a considerable photocurrent under illumination with a 405 nm modulated diode laser at comparatively high frequencies and low applied DC potentials, making this a promising substrate for bioimaging applications. Linear sweep voltammetry showed negligible dark currents. The imaging capabilities of the sensor substrate were demonstrated with a model system and showed a lateral resolution of 7 microns.
Keywords: InGaN/GaN epilayer; cell imaging; light-activated electrochemistry; light-addressable potentiometric sensor; photoelectrochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mourzina Y., Yoshinobu T., Schubert J., Lüth H., Iwasaki H., Schöning M.J. Ion-selective light-addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS) with chalcogenide thin film prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001;80:136–140. doi: 10.1016/S0925-4005(01)00906-6. - DOI
-
- Oba N., Yoshinobu T., Iwasaki H. Redox Potential Imaging Sensor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1996;35:460–463. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.35.L460. - DOI
-
- Seki A., Ikeda S., Kubo I., Karube I. Biosensors based on light-addressable potentiometric sensors for urea, penicillin and glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1998;373:9–13. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(98)00364-X. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

