Eco-Friendly β-cyclodextrin and Linecaps Polymers for the Removal of Heavy Metals
- PMID: 31614648
- PMCID: PMC6835710
- DOI: 10.3390/polym11101658
Eco-Friendly β-cyclodextrin and Linecaps Polymers for the Removal of Heavy Metals
Abstract
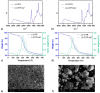
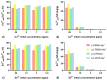
Environment-friendly nanosponges, having a high content of carboxyl groups, were synthesized by crosslinking β-cyclodextrin and linecaps, a highly soluble pea starch derivative, with citric acid in water. Additionally, pyromellitic nanosponges were prepared by reacting β-cyclodextrin and linecaps with pyromellitic dianhydride in dimethyl sulfoxide and used in comparison with the citric nanosponges. After ion-exchange of the carboxyl groups H+ with sodium ions, the ability of the nanosponges to sequester heavy metal cations was investigated. At a metal concentration of 500 ppm, the pyromellitate nanosponges exhibited a higher retention capacity than the citrate nanosponges. At lower metal concentrations (≤50 ppm) both the citrate and the pyromellitate nanosponges showed high retention capacities (up to 94% of the total amount of metal), while, in the presence of interfering sea water salts, the citrate nanosponges were able to selectively adsorb a significantly higher amount of heavy metals than the pyromellitate nanosponges, almost double in the case of Cu2+.
Keywords: citric acid polymers; crosslinked polymers; heavy metal adsorption; linecaps; nanosponge; β-cyclodextrin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
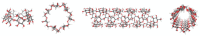




References
-
- Wang L.K., Chen J.P., Hung Y.-T., Shammas N.K. Heavy Metals in the Environment. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2017.
-
- Chen J.P. Decontamination of Heavy Metals: Processes, Mechanisms, and Applications. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2012.
-
- Gerhardsson L., Kazantzis G. Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals. 4th ed. Academic Press; London, UK: 2015. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metal Poisoning: General Aspects; pp. 487–505. Chapter 23.
-
- Wijayawardena M.A.A., Megharaj M., Naidu R. Advances in Agronomy. Academic Press; London, UK: 2016. Exposure, Toxicity, Health Impacts, and Bioavailability of Heavy Metal Mixtures. Chapter 3.

