Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: Manufacturing, Properties, and Applications
- PMID: 31614875
- PMCID: PMC6835861
- DOI: 10.3390/polym11101667
Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: Manufacturing, Properties, and Applications
Abstract
Composites have been found to be the most promising and discerning material available in this century. Presently, composites reinforced with fibers of synthetic or natural materials are gaining more importance as demands for lightweight materials with high strength for specific applications are growing in the market. Fiber-reinforced polymer composite offers not only high strength to weight ratio, but also reveals exceptional properties such as high durability; stiffness; damping property; flexural strength; and resistance to corrosion, wear, impact, and fire. These wide ranges of diverse features have led composite materials to find applications in mechanical, construction, aerospace, automobile, biomedical, marine, and many other manufacturing industries. Performance of composite materials predominantly depends on their constituent elements and manufacturing techniques, therefore, functional properties of various fibers available worldwide, their classifications, and the manufacturing techniques used to fabricate the composite materials need to be studied in order to figure out the optimized characteristic of the material for the desired application. An overview of a diverse range of fibers, their properties, functionality, classification, and various fiber composite manufacturing techniques is presented to discover the optimized fiber-reinforced composite material for significant applications. Their exceptional performance in the numerous fields of applications have made fiber-reinforced composite materials a promising alternative over solitary metals or alloys.
Keywords: composite materials; fiber-reinforced polymer; natural fibers; synthetic fibers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




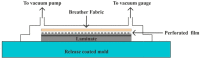
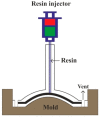
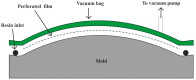
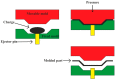
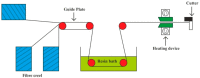
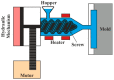
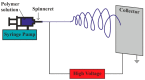



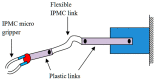



References
-
- Yashas Gowda T.G., Sanjay M.R., Subrahmanya Bhat K., Madhu P., Senthamaraikannan P., Yogesha B. SSPolymer matrix-natural fiber composites: An overview. Cogent. Eng. 2018;5:1446667. doi: 10.1080/23311916.2018.1446667. - DOI
-
- Linul E., Lell D., Movahedi N., Codrean C., Fiedler T. Compressive properties of Zinc Syntactic Foams at elevated temperatures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019;167:122–134. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.12.019. - DOI
-
- Clyne T.W., Hull D. An Introduction to Composite Materials. 3rd ed. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2019.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

