Graphene Oxide Enhances Chitosan-Based 3D Scaffold Properties for Bone Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 31614903
- PMCID: PMC6834324
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20205077
Graphene Oxide Enhances Chitosan-Based 3D Scaffold Properties for Bone Tissue Engineering
Abstract
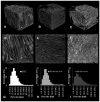
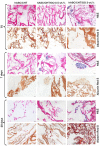
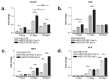
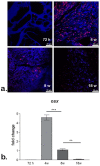
The main goal of bone tissue engineering (BTE) is to refine and repair major bone defects based on bioactive biomaterials with distinct properties that can induce and support bone tissue formation. Graphene and its derivatives, such as graphene oxide (GO), display optimal properties for BTE, being able to support cell growth and proliferation, cell attachment, and cytoskeleton development as well as the activation of osteogenesis and bone development pathways. Conversely, the presence of GO within a polymer matrix produces favorable changes to scaffold morphologies that facilitate cell attachment and migration i.e., more ordered morphologies, greater surface area, and higher total porosity. Therefore, there is a need to explore the potential of GO for tissue engineering applications and regenerative medicine. Here, we aim to promote one novel scaffold based on a natural compound of chitosan, improved with 3 wt.% GO, for BTE approaches, considering its good biocompatibility, remarkable 3D characteristics, and ability to support stem cell differentiation processes towards the bone lineage.
Keywords: biocompatibility; bone tissue engineering; graphene oxide; human adipose-derived stem cells; osteogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PNIII-P1.1.2- PCCDI-2017-0782/ REGMED/Romanian Ministry of Research and Innovation, CCCDI-UEFISCDI
- 154/25.11.2016, P_37_221/2015, SMIS code 108117/Ministry of Research and Innovation, Operational Program Competitiveness Axis 1 533 - Section E, Program co-financed from European Regional Development Fund
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

