Developmentally regulated KCC2 phosphorylation is essential for dynamic GABA-mediated inhibition and survival
- PMID: 31615901
- PMCID: PMC7219477
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.aaw9315
Developmentally regulated KCC2 phosphorylation is essential for dynamic GABA-mediated inhibition and survival
Abstract
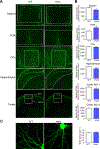
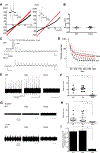
Despite its importance for γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) inhibition and involvement in neurodevelopmental disease, the regulatory mechanisms of the K+/Cl- cotransporter KCC2 (encoded by SLC12A5) during maturation of the central nervous system (CNS) are not entirely understood. Here, we applied quantitative phosphoproteomics to systematically map sites of KCC2 phosphorylation during CNS development in the mouse. KCC2 phosphorylation at Thr906 and Thr1007, which inhibits KCC2 activity, underwent dephosphorylation in parallel with the GABA excitatory-inhibitory sequence in vivo. Knockin mice expressing the homozygous phosphomimetic KCC2 mutations T906E/T1007E (Kcc2E/E ), which prevented the normal developmentally regulated dephosphorylation of these sites, exhibited early postnatal death from respiratory arrest and a marked absence of cervical spinal neuron respiratory discharges. Kcc2E/E mice also displayed disrupted lumbar spinal neuron locomotor rhythmogenesis and touch-evoked status epilepticus associated with markedly impaired KCC2-dependent Cl- extrusion. These data identify a previously unknown phosphorylation-dependent KCC2 regulatory mechanism during CNS development that is essential for dynamic GABA-mediated inhibition and survival.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Tuning the regulator: Phosphorylation of KCC2 at two specific sites is critical for neurodevelopment.Sci Signal. 2019 Oct 15;12(603):eaay8960. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aay8960. Sci Signal. 2019. PMID: 31615900
References
-
- Farrant M, and Kaila K. 2007. The cellular, molecular and ionic basis of GABA(A) receptor signalling. Progress in brain research 160: 59–87. - PubMed
-
- Nakanishi K, Yamada J, Takayama C, Oohira A, and Fukuda A. 2007. NKCC1 activity modulates formation of functional inhibitory synapses in cultured neocortical neurons. Synapse (New York, N.Y 61: 138–149. - PubMed
-
- Behar TN, Schaffner AE, Scott CA, Greene CL, and Barker JL. 2000. GABA receptor antagonists modulate postmitotic cell migration in slice cultures of embryonic rat cortex. Cereb Cortex 10: 899–909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

