System-Wide Characterization of MoArf GTPase Family Proteins and Adaptor Protein MoGga1 Involved in the Development and Pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae
- PMID: 31615964
- PMCID: PMC6794486
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.02398-19
System-Wide Characterization of MoArf GTPase Family Proteins and Adaptor Protein MoGga1 Involved in the Development and Pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae
Abstract
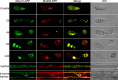
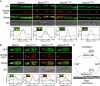
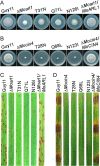
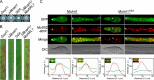
ADP ribosylation factor (Arf) small GTPase family members are involved in vesicle trafficking and organelle maintenance in organisms ranging from Saccharomyces cerevisiae to humans. A previous study identified Magnaporthe oryzae Arf6 (MoArf6) as one of the Arf proteins that regulates growth and conidiation in the rice blast fungus M. oryzae, but the remaining family proteins remain unknown. Here, we identified six additional Arf proteins, including MoArf1, MoArl1, MoArl3, MoArl8, MoCin4, and MoSar1, as well as their sole adaptor protein, MoGga1, and determined their shared and specific functions. We showed that the majority of these proteins exhibit positive regulatory functions, most notably, in growth. Importantly, MoArl1, MoCin4, and MoGga1 are involved in pathogenicity through the regulation of host penetration and invasive hyphal growth. MoArl1 and MoCin4 also regulate normal vesicle trafficking, and MoCin4 further controls the formation of the biotrophic interfacial complex (BIC). Moreover, we showed that Golgi-cytoplasm cycling of MoArl1 is required for its function. Finally, we demonstrated that interactions between MoArf1 and MoArl1 with MoGga1 are important for Golgi localization and pathogenicity. Collectively, our findings revealed the shared and specific functions of Arf family members in M. oryzae and shed light on how these proteins function through conserved mechanisms to govern growth, transport, and virulence of the blast fungus.IMPORTANCEMagnaporthe oryzae is the causal agent of rice blast, representing the most devastating diseases of rice worldwide, which results in losses of amounts of rice that could feed more than 60 million people each year. Arf (ADP ribosylation factor) small GTPase family proteins are involved in vesicle trafficking and organelle maintenance in eukaryotic cells. To investigate the function of Arf family proteins in M. oryzae, we systematically characterized all seven Arf proteins and found that they have shared and specific functions in governing the growth, development, and pathogenicity of the blast fungus. We have also identified the pathogenicity-related protein MoGga1 as the common adaptor of MoArf1 and MoArl1. Our findings are important because they provide the first comprehensive characterization of the Arf GTPase family proteins and their adaptor protein MoGga1 functioning in a plant-pathogenic fungus, which could help to reveal new fungicide targets to control this devastating disease.
Keywords: ADP ribosylation factor; Golgi; Magnaporthe oryzae; pathogenicity; vesicle trafficking.
Copyright © 2019 Zhang et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The ArfGAP protein MoGlo3 regulates the development and pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae.Environ Microbiol. 2017 Oct;19(10):3982-3996. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13798. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28504350 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of 47 Cys2 -His2 zinc finger proteins required for the development and pathogenicity of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae.New Phytol. 2016 Aug;211(3):1035-51. doi: 10.1111/nph.13948. Epub 2016 Apr 4. New Phytol. 2016. PMID: 27041000
-
The syntaxin protein (MoSyn8) mediates intracellular trafficking to regulate conidiogenesis and pathogenicity of rice blast fungus.New Phytol. 2016 Mar;209(4):1655-67. doi: 10.1111/nph.13710. Epub 2015 Nov 2. New Phytol. 2016. PMID: 26522477
-
Effector-triggered susceptibility by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae.New Phytol. 2024 Feb;241(3):1007-1020. doi: 10.1111/nph.19446. Epub 2023 Dec 10. New Phytol. 2024. PMID: 38073141 Review.
-
Regulation of Autophagy Machinery in Magnaporthe oryzae.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 28;23(15):8366. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158366. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955497 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The COPII subunit MoSec24B is involved in development, pathogenicity and autophagy in the rice blast fungus.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jan 9;13:1074107. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1074107. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36699840 Free PMC article.
-
Auxilin-like protein MoSwa2 promotes effector secretion and virulence as a clathrin uncoating factor in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae.New Phytol. 2021 Apr;230(2):720-736. doi: 10.1111/nph.17181. Epub 2021 Feb 13. New Phytol. 2021. PMID: 33423301 Free PMC article.
-
MoIug4 is a novel secreted effector promoting rice blast by counteracting host OsAHL1-regulated ethylene gene transcription.New Phytol. 2022 Aug;235(3):1163-1178. doi: 10.1111/nph.18169. Epub 2022 May 21. New Phytol. 2022. PMID: 35451078 Free PMC article.
-
The rice blast fungus MoRgs1 functioning in cAMP signaling and pathogenicity is regulated by casein kinase MoCk2 phosphorylation and modulated by membrane protein MoEmc2.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jun 16;17(6):e1009657. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009657. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34133468 Free PMC article.
-
MoLrp1-mediated signaling induces nuclear accumulation of MoMsn2 to facilitate fatty acid oxidation for infectious growth of the rice blast fungus.Plant Commun. 2023 Jul 10;4(4):100561. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2023.100561. Epub 2023 Feb 11. Plant Commun. 2023. PMID: 36774535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosch DE, Willard FS, Ramanujam R, Kimple AJ, Willard MD, Naqvi NI, Siderovski DP. 2012. A P-loop mutation in Galpha subunits prevents transition to the active state: implications for G-protein signaling in fungal pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002553. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002553. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

