The Association between the Comprehensive Epstein-Barr Virus Serologic Profile and Endemic Burkitt Lymphoma
- PMID: 31619404
- PMCID: PMC6954331
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-19-0551
The Association between the Comprehensive Epstein-Barr Virus Serologic Profile and Endemic Burkitt Lymphoma
Abstract
Background: The discovery of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in Burkitt lymphoma tumors represented the first link between a virus and cancer in humans, but the underlying role of this virus in endemic Burkitt lymphoma remains unclear. Nearly all children in Burkitt lymphoma-endemic areas are seropositive for EBV, but only a small percentage develop disease. Variation in EBV-directed immunity could be an explanatory cofactor.
Methods: We examined serum from 150 Burkitt lymphoma cases and 150 controls using a protein microarray that measured IgG and IgA antibodies against 202 sequences across the entire EBV proteome. Variation in the EBV-directed antibody repertoire between Burkitt lymphoma cases and controls was assessed using unpaired t tests. ORs quantifying the association between anti-EBV IgG response tertiles and Burkitt lymphoma status were adjusted for age, sex, and study year.
Results: Thirty-three anti-EBV IgG responses were elevated in Burkitt lymphoma cases compared with controls (P ≤ 0.0003). Burkitt lymphoma-associated IgG elevations were strongest for EBV proteins involved in viral replication and antiapoptotic signaling. Specifically, we observed ORs ≥4 for BMRF1 (early antigen), BBLF1 (tegument protein), BHRF1 (Bcl-2 homolog), BZLF1 (Zebra), BILF2 (glycoprotein), BLRF2 [viral capsid antigen (VCA)p23], BDLF4, and BFRF3 (VCAp18). Adjustment for malaria exposure and inheritance of the sickle cell variant did not alter associations.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that the anti-EBV serologic profile in patients with Burkitt lymphoma is altered, with strong elevations in 33 of the measured anti-EBV IgG antibodies relative to disease-free children.
Impact: The Burkitt lymphoma-specific signature included EBV-based markers relevant for viral replication and antiapoptotic activity, providing clues for future Burkitt lymphoma pathogenesis research.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
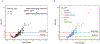
References
-
- Epstein MA, Achong BG, Barr YM. Virus Particles in Cultured Lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s Lymphoma. Lancet 1964;1(7335):702–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

