A modulator of wild-type glucocerebrosidase improves pathogenic phenotypes in dopaminergic neuronal models of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 31619543
- PMCID: PMC7359409
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau6870
A modulator of wild-type glucocerebrosidase improves pathogenic phenotypes in dopaminergic neuronal models of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
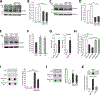
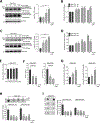
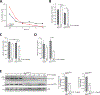
Mutations in the GBA1 gene encoding the lysosomal enzyme β-glucocerebrosidase (GCase) represent the most common risk factor for Parkinson's disease (PD). GCase has been identified as a potential therapeutic target for PD and current efforts are focused on chemical chaperones to translocate mutant GCase into lysosomes. However, for several GBA1-linked forms of PD and PD associated with mutations in LRRK2, DJ-1, and PARKIN, activating wild-type GCase represents an alternative approach. We developed a new small-molecule modulator of GCase called S-181 that increased wild-type GCase activity in iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons from sporadic PD patients, as well as patients carrying the 84GG mutation in GBA1, or mutations in LRRK2, DJ-1, or PARKIN who had decreased GCase activity. S-181 treatment of these PD iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons partially restored lysosomal function and lowered accumulation of oxidized dopamine, glucosylceramide and α-synuclein. Moreover, S-181 treatment of mice heterozygous for the D409V GBA1 mutation (Gba1D409V/+ ) resulted in activation of wild-type GCase and consequent reduction of GCase lipid substrates and α-synuclein in mouse brain tissue. Our findings point to activation of wild-type GCase by small-molecule modulators as a potential therapeutic approach for treating familial and sporadic forms of PD that exhibit decreased GCase activity.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
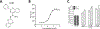

References
-
- Sidransky E, Nalls MA, Aasly JO, Aharon-Peretz J, Annesi G, Barbosa ER, Bar-Shira A, Berg D, Bras J, Brice A, Chen CM, Clark LN, Condroyer C, De Marco EV, Durr A, Eblan MJ, Fahn S, Farrer MJ, Fung HC, Gan-Or Z, Gasser T, Gershoni-Baruch R, Giladi N, Griffith A, Gurevich T, Januario C, Kropp P, Lang AE, Lee-Chen GJ, Lesage S, Marder K, Mata IF, Mirelman A, Mitsui J, Mizuta I, Nicoletti G, Oliveira C, Ottman R, Orr-Urtreger A, Pereira LV, Quattrone A, Rogaeva E, Rolfs A, Rosenbaum H, Rozenberg R, Samii A, Samaddar T, Schulte C, Sharma M, Singleton A, Spitz M, Tan EK, Tayebi N, Toda T, Troiano AR, Tsuji S, Wittstock M, Wolfsberg TG, Wu YR, Zabetian CP, Zhao Y, Ziegler SG, Multicenter analysis of glucocerebrosidase mutations in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 361, 1651–1661 (2009); published online EpubOct 22 (10.1056/NEJMoa0901281). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mazzulli JR, Xu YH, Sun Y, Knight AL, McLean PJ, Caldwell GA, Sidransky E, Grabowski GA, Krainc D, Gaucher disease glucocerebrosidase and alpha-synuclein form a bidirectional pathogenic loop in synucleinopathies. Cell 146, 37–52 (2011); published online EpubJul 8 (10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.001). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

