Ixekizumab Results in Persistent Clinical Improvement in Moderate-to-Severe Genital Psoriasis During a 52 Week, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Clinical Trial
- PMID: 31620802
- PMCID: PMC9128873
- DOI: 10.2340/00015555-3353
Ixekizumab Results in Persistent Clinical Improvement in Moderate-to-Severe Genital Psoriasis During a 52 Week, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Clinical Trial
Abstract
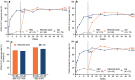
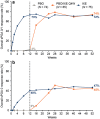
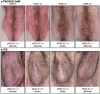
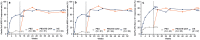
Ixekizumab was efficacious in treating moderate-to-severe genital psoriasis over 12 weeks. We evaluated the long-term efficacy and safety of ixekizumab for up to 52 weeks. Patients were randomized to 80 mg ixekizumab every 2 weeks or to placebo through Week 12, then received 80 mg open-label ixekizumab every 4 weeks through Week 52. In patients initially randomized to ixekizumab, clear or almost clear genital skin was achieved for 73% of patients at Week 12 and 75% at Week 52. Persistent improvements were also observed for overall psoriasis, genital itch, and the impact of genital psoriasis on the frequency of sexual activity. The safety profile was consistent with studies of ixekizumab in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Ixekizumab provided rapid and persistent improvements in the signs and symptoms of genital psoriasis for up to 52 weeks of treatment.
Keywords: IXORA-Q; clinical trial; genital psoriasis; itch; ixekizumab; sexual impact.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Meeuwis KAP, Potts Bleakman A, van de Kerkhof PCM, Dutronc Y, Henneges C, Kornberg LJ, et al. . Prevalence of genital psoriasis in patients with psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat 2018; 29: 1–7. - PubMed
-
- Ryan C, Sadlier M, De Vol E, Patel M, Lloyd AA, Day A, et al. . Genital psoriasis is associated with significant impairment in quality of life and sexual functioning. J Am Acad Dermatol 2015; 72: 978–983. - PubMed
-
- Meeuwis KA, de Hullu JA, Massuger LF, van de Kerkhof PC, van Rossum MM. Genital psoriasis: A systematic literature review on this hidden skin disease. Acta Derm Venereol 2011; 91: 5–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

