Reported β-Lactam and Other Antibiotic Allergies in Solid Organ and Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 31621829
- PMCID: PMC8241219
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciz1025
Reported β-Lactam and Other Antibiotic Allergies in Solid Organ and Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients
Abstract
Background: Patients with reported β-lactam antibiotic allergies (BLAs) are more likely to receive broad-spectrum antibiotics and experience adverse outcomes. Data describing antibiotic allergies among solid organ transplant (SOT) and hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) recipients are limited.
Methods: We reviewed records of adult SOT or allogeneic HCT recipients from 1 January 2013 to 31 December 2017 to characterize reported antibiotic allergies at time of transplantation. Inpatient antibiotic use was examined for 100 days posttransplant. Incidence rate ratios (IRRs) comparing antibiotic use in BLA and non-BLA groups were calculated using multivariable negative binomial models for 2 metrics: days of therapy (DOT) per 1000 inpatient days and percentage of antibiotic exposure-days.
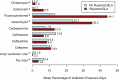
Results: Among 2153 SOT (65%) and HCT (35%) recipients, 634 (29%) reported any antibiotic allergy and 347 (16%) reported BLAs. Inpatient antibiotics were administered to 2020 (94%) patients during the first 100 days posttransplantation; average antibiotic exposure was 41% of inpatient-days (interquartile range, 16.7%-62.5%). BLA patients had significantly higher DOT for vancomycin (IRR, 1.4 [95% confidence interval {CI}, 1.2-1.7]; P < .001), clindamycin (IRR, 7.6 [95% CI, 2.2-32.4]; P = .001), and aztreonam in HCT (IRR, 9.7 [95% CI, 3.3-35.0]; P < .001), and fluoroquinolones in SOT (IRR, 2.9 [95% CI, 2.1-4.0]; P < .001); these findings were consistent when using percentage of antibiotic exposure-days.
Conclusions: Transplant recipients are frequently exposed to antibiotics and have a high prevalence of reported antibiotic allergies. Reported BLA was associated with greater use of β-lactam antibiotic alternatives. Pretransplant antibiotic allergy evaluation may optimize antibiotic use in this population.
Keywords: allergy; hematopoietic cell transplantation; solid organ transplantation; β-lactams.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Lee CE, Zembower TR, Fotis MA, et al. The incidence of antimicrobial allergies in hospitalized patients: implications regarding prescribing patterns and emerging bacterial resistance. Arch Intern Med 2000; 160:2819–22. - PubMed
-
- Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters; American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Drug allergy: an updated practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2010; 105:259–73. - PubMed
-
- Macy E, Contreras R. Adverse reactions associated with oral and parenteral use of cephalosporins: a retrospective population-based analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015; 135:745–52.e5. - PubMed
-
- Macy E, Contreras R. Health care use and serious infection prevalence associated with penicillin “allergy” in hospitalized patients: a cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2014; 133:790–6. - PubMed
-
- MacFadden DR, LaDelfa A, Leen J, et al. Impact of reported beta-lactam allergy on inpatient outcomes: a multicenter prospective cohort study. Clin Infect Dis 2016; 63:904–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

