Spermatogonial Type 3 Deiodinase Regulates Thyroid Hormone Target Genes in Developing Testicular Somatic Cells
- PMID: 31621880
- PMCID: PMC6853691
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2019-00259
Spermatogonial Type 3 Deiodinase Regulates Thyroid Hormone Target Genes in Developing Testicular Somatic Cells
Erratum in
-
WITHDRAWN AS DUPLICATE: Spermatogonial Type 3 Deiodinase Regulates Thyroid Hormone Target Genes in Developing Testicular Somatic Cells.Endocrinology. 2020 Feb 1;161(2):bqz001. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqz001. Endocrinology. 2020. PMID: 32639012 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
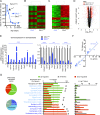
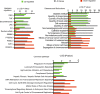
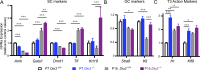
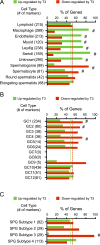
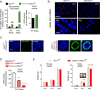
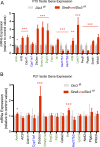
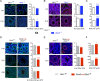
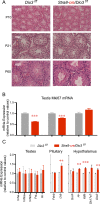
Premature overexposure to thyroid hormone causes profound effects on testis growth, spermatogenesis, and male fertility. We used genetic mouse models of type 3 deiodinase (DIO3) deficiency to determine the genetic programs affected by premature thyroid hormone action and to define the role of DIO3 in regulating thyroid hormone economy in testicular cells. Gene expression profiling in the neonatal testis of DIO3-deficient mice identified 5699 differentially expressed genes. Upregulated and downregulated genes were, respectively, involved according to DAVID analysis with cell differentiation and proliferation. They included anti-Müllerian hormone and genes involved in the formation of the blood-testis barrier, which are specific to Sertoli cells (SCs). They also included steroidogenic genes, which are specific to Leydig cells. Comparison with published data sets of genes enriched in SCs and spermatogonia, and responsive to retinoic acid (RA), identified a subset of genes that were regulated similarly by RA and thyroid hormone. This subset of genes showed an expression bias, as they were downregulated when enriched in spermatogonia and upregulated when enriched in SCs. Furthermore, using a genetic approach, we found that DIO3 is not expressed in SCs, but spermatogonia-specific inactivation of DIO3 led to impaired testis growth, reduced SC number, decreased cell proliferation and, especially during neonatal development, altered gene expression specific to somatic cells. These findings indicate that spermatogonial DIO3 protects testicular cells from untimely thyroid hormone signaling and demonstrate a mechanism of cross-talk between somatic and germ cells in the neonatal testis that involves the regulation of thyroid hormone availability and action.
Copyright © 2019 Endocrine Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thyroid hormone action in the developing testis: intergenerational epigenetics.J Endocrinol. 2020 Feb 17;244(3):R33-R46. doi: 10.1530/JOE-19-0550. J Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 31977317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid Hormone Role and Economy in the Developing Testis.Vitam Horm. 2018;106:473-500. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2017.06.005. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Vitam Horm. 2018. PMID: 29407445 Review.
-
Gonadotrophin-mediated miRNA expression in testis at onset of puberty in rhesus monkey: predictions on regulation of thyroid hormone activity and DLK1-DIO3 locus.Mol Hum Reprod. 2019 Mar 1;25(3):124-136. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gay054. Mol Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 30590698 Free PMC article.
-
Spermatogonial Dio3 as a potential germ line sensor for thyroid hormone-driven epigenetic inheritance †.Biol Reprod. 2021 Sep 14;105(3):613-615. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioab089. Biol Reprod. 2021. PMID: 33962462 Free PMC article.
-
Adult onset of type 3 deiodinase deficiency in mice alters brain gene expression and increases locomotor activity.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019 Dec;110:104439. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.104439. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019. PMID: 31561084 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic developmental programming and intergenerational effects of thyroid hormones.Vitam Horm. 2023;122:23-49. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2023.01.003. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Vitam Horm. 2023. PMID: 36863795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid hormone elicits intergenerational epigenetic effects on adult social behavior and fetal brain expression of autism susceptibility genes.Front Neurosci. 2022 Nov 7;16:1055116. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1055116. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36419462 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid Hormone Clearance in the Paraventricular Nucleus of Male Mice Regulates Lean Mass and Physical Activity.Neuroendocrinology. 2024;114(11):1066-1076. doi: 10.1159/000541525. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Neuroendocrinology. 2024. PMID: 39293416
-
Thyroid hormone action in the developing testis: intergenerational epigenetics.J Endocrinol. 2020 Feb 17;244(3):R33-R46. doi: 10.1530/JOE-19-0550. J Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 31977317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of thyroid and leptin hormones and their crosstalk in male reproductive functions: an updated review.Endocrine. 2025 Mar;87(3):891-906. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-04069-8. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Endocrine. 2025. PMID: 39412610 Review.
References
-
- Picut CA, Remick AK, de Rijk EP, Simons ML, Stump DG, Parker GA. Postnatal development of the testis in the rat: morphologic study and correlation of morphology to neuroendocrine parameters. Toxicol Pathol. 2015;43(3):326–342. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez A. Thyroid hormone role and economy in the developing testis. Vitam Horm. 2018;106:473–500. - PubMed
-
- Bunick D, Kirby J, Hess RA, Cooke PS. Developmental expression of testis messenger ribonucleic acids in the rat following propylthiouracil-induced neonatal hypothyroidism. Biol Reprod. 1994;51(4):706–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

