Safety lead-in of the MEK inhibitor trametinib in combination with GSK2141795, an AKT inhibitor, in patients with recurrent endometrial cancer: An NRG Oncology/GOG study
- PMID: 31623857
- PMCID: PMC6922584
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2019.09.024
Safety lead-in of the MEK inhibitor trametinib in combination with GSK2141795, an AKT inhibitor, in patients with recurrent endometrial cancer: An NRG Oncology/GOG study
Abstract
Objective: We sought to determine safety and efficacy of the AKT inhibitor, GSK2141795, combined with the MEK inhibitor, trametinib, in endometrial cancer.
Methods: Patients with measurable recurrent endometrial cancer were eligible. One to two prior cytotoxic regimens were allowed; prior use of a MEK or PI3K pathway inhibitor was excluded. Initial trial design consisted of a KRAS mutation stratified randomized phase II with a safety lead-in evaluating the combination. For the safety lead in, the previously recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D; trametinib 1.5 mg, GSK2141795 50 mg) was chosen for Dose Level 1 (DL1).
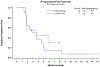
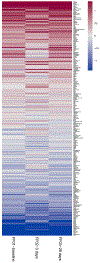
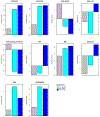
Results: Of 26 enrolled patients, 14 were treated on DL1 and 12 were treated on DL-1 (trametinib 1.5 mg, GSK2141795 25 mg). Most common histologies were endometrioid (58%) and serous (27%). Four of 25 (16%) patients were KRAS mutant. Dose limiting toxicities (DLTs) were assessed during cycle 1. DL1 had 8 DLTs (hypertension (n = 2), mucositis (2), rash (2), dehydration, stroke/acute kidney injury). DL1 was deemed non-tolerable so DL-1 was explored. DL-1 had no DLTs. Sixty-five percent of patients had ≥ grade 3 toxicity. There were no responses in DL1 (0%, 90%CI 0-15%) and 1 response in DL-1 (8.3%, 90%CI 0.4-33.9%). Proportion PFS at 6 months for DL1 is 14%, and 25% for DL-1.
Conclusion: The combination of trametinib and GSK2141795 had high levels of toxicity in endometrial cancer at the previously RP2D but was tolerable at a reduced dose. Due to insufficient preliminary efficacy at a tolerable dose, the Phase II study was not initiated.
Keywords: AKT inhibition; Endometrial cancer; KRAS mutation; MEK inhibition; NRG oncology; PI3K.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Shannon Westin reports that she has received research support from ArQule, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Tesaro, Bayer, Roche/Genentech, Cotinga Pharmaceuticals and Novartis. In addition, Dr. Westin has served as Consultant for AstraZeneca, Clovis, Tesaro, Bayer, Novartis, Roche/Genentech, Pfizer, Takeda and Merck.
Drs. Sill, Ju, Waggoner, Birrer, Modesitt, Mathews, Schilder and Lee have no conflict of interest to declare.
Dr. Robert Coleman reports research funding from AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Clovis, Roche/Genentech, Janssen and Merck. Dr. Coleman has served on the Scientific Steering Committee for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Immunogen, Tesaro, Array, Janssen, Genmab and Gamamab.
Dr. Kathleen Moore reports that she served on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Advaxis, Clovis, Immunogen, Jannsen, Genentech/Roche, Aravive, VBL Therapeutics, OncoMed, Tesaro and Merck (all honoraria paid to Dr. Moore). Dr. Moore reports serving on steering committees for Genentech Roche, Tesaro, Immunogen and Aravive (unpaid).
Dr. Lainie Martin reports that she has served on advisory boards for ImmunoGen and Tesaro.
Dr. Gordon Mills reports that he has served on Scientific Advisory boards or as consultant for AstraZeneca, Catena Pharmaceuticals, Critical Outcome Technologies, ImmunoMET, Ionis, Signalchem Lifesciences, Symphogen and Takeda/Millennium Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Mills reports that he has Tarveda, Stock options/financial Catena Pharmaceuticals, ImmunoMet, SignalChem, Spindle Top Ventures, Tarveda. He also has licensed technology HRD assay to Myriad Genetics, DSP patent with Nanostring. Additionally, Dr. Mills has sponsored research performed for Adelson Medical Research Foundation, AstraZeneca, Breast Cancer Research Foundation, Immunomet, Ionis, Komen Research Foundation, Nanostring, Ovarian Cancer Research Foundation, Pfizer, Prospect Creek Foundation and Takeda/Millennium Pharmaceuticals.
Dr. Paula Fracasso reports that she has no conflicts to disclose. Dr. Fracasso worked on this study while employed by the University of Virginia and, since May of 2014, has been an employee of Bristol-Myers Squibb and has stock with the company.
Dr. Carol Aghajanian reports personal fees from Tesaro, personal fees from Immunogen, personal fees from Clovis, personal fees from Mateon Therapeutics, personal fees from Cerulean Pharmaceutical, outside of the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 2017; 67(1): 7–30. - PubMed
-
- Burke WM, Orr J, Leitao M, et al. Endometrial cancer: a review and current management strategies: part II. Gynecol Oncol 2014; 134(2): 393–402. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Uterine Neoplasms. 2017. (accessed April 25 2017).
-
- Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y, Mills GB. Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2005; 4(12): 988–1004. - PubMed
-
- West KA, Castillo SS, Dennis PA. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and chemotherapeutic resistance. Drug Resist Updat 2002; 5(6): 234–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

