Patient-Tailored, Connectivity-Based Forecasts of Spreading Brain Atrophy
- PMID: 31623919
- PMCID: PMC7012373
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.08.037
Patient-Tailored, Connectivity-Based Forecasts of Spreading Brain Atrophy
Abstract
Neurodegenerative diseases appear to progress by spreading via brain connections. Here we evaluated this transneuronal degeneration hypothesis by attempting to predict future atrophy in a longitudinal cohort of patients with behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD) and semantic variant primary progressive aphasia (svPPA). We determined patient-specific "epicenters" at baseline, located each patient's epicenters in the healthy functional connectome, and derived two region-wise graph theoretical metrics to predict future atrophy: (1) shortest path length to the epicenter and (2) nodal hazard, the cumulative atrophy of a region's first-degree neighbors. Using these predictors and baseline atrophy, we could accurately predict longitudinal atrophy in most patients. The regions most vulnerable to subsequent atrophy were functionally connected to the epicenter and had intermediate levels of baseline atrophy. These findings provide novel, longitudinal evidence that neurodegeneration progresses along connectional pathways and, further developed, could lead to network-based clinical tools for prognostication and disease monitoring.
Keywords: brain networks; frontotemporal dementia; functional connectivity; graph theory; neurodegeneration; voxel-based morphometry.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


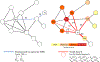

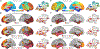
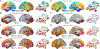
References
-
- Ashburner J, and Friston KJ (2005). Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 26, 839–851. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG058233/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052943/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062422/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS100440/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG055698/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG052648/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DC015544/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG055121/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS050915/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050915/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States

