Vazirani-Akinosi Nerve Block Technique: An Asset of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon
- PMID: 31624448
- PMCID: PMC6795644
- DOI: 10.1007/s12663-019-01183-3
Vazirani-Akinosi Nerve Block Technique: An Asset of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon
Abstract
Background: Vazirani-Akinosi nerve block technique is an established and a reliable technique to achieve anaesthesia in mandible with high success rate and is useful in cases where Halstead's technique fails to provide desired anaesthetic effect.
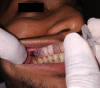
Materials and methods: A total of 140 ASA-I or ASA-II patients, both genders, between 16 and 45 years who required extraction of mandibular tooth were divided into two groups. Group A received nerve block through Halstead technique, while Group B received nerve block through Vazirani-Akinosi technique with 2% lignocaine containing 1:200,000 adrenaline. We evaluated the subjective and objective onset of anaesthesia, outcome of the injection, outcome of the aspiration and patient satisfaction.
Results: In Group A, the altered sensation was experienced at 68.70 s, while in Group B it was 92.55 s and the difference was statistically highly significant (p < 0.001) between the two groups. The mean onset of anaesthesia (measured with Electric pulp tester) in Group A was 78.36 s, while for Group B it was 104.24 s and this difference was statistically highly significant (p < 0.001). Positive aspiration was seen in 11 (15.71%) patients in Group A and in 2 (2.86%) patients in Group B. The success rate for Group A was 81.42% and for Group B it was 97.14%.
Conclusion: Vazirani-Akinosi technique provides desirable surgical anaesthesia with relatively high success rate and lower incidence of positive aspiration and can be considered as a boon for oral and maxillofacial surgeons.
Keywords: Closed mouth technique; Halstead technique; Inferior alveolar nerve block; Vazirani–Akinosi technique.
© The Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons of India 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Malamed SF. Handbook of local anesthesia. 6. St. Louis: Mosby; 2013.
-
- McLure HA, Rubin AP. Review of local anaesthetic agents. Min Anestesiol. 2005;71(3):59–74. - PubMed
-
- Bennett CR. Monheim’s local anesthesia and pain control in dental practice. 7. Hamilton: B.C. Decker; 1990.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
