The Bellerophon pipeline, improving de novo transcriptomes and removing chimeras
- PMID: 31624564
- PMCID: PMC6787812
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.5571
The Bellerophon pipeline, improving de novo transcriptomes and removing chimeras
Abstract
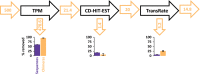
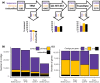
Transcriptome quality control is an important step in RNA-Seq experiments. However, the quality of de novo assembled transcriptomes is difficult to assess, due to the lack of reference genome to compare the assembly to. We developed a method to assess and improve the quality of de novo assembled transcriptomes by focusing on the removal of chimeric sequences. These chimeric sequences can be the result of faulty assembled contigs, merging two transcripts into one. The developed method is incorporated into a pipeline, which we named Bellerophon, that is broadly applicable and easy to use. Bellerophon first uses the quality assessment tool TransRate to indicate the quality, after which it uses a transcripts per million (TPM) filter to remove lowly expressed contigs and CD-HIT-EST to remove highly identical contigs. To validate the quality of this method, we performed three benchmark experiments: (1) a computational creation of chimeras, (2) identification of chimeric contigs in a transcriptome assembly, (3) a simulated RNA-Seq experiment using a known reference transcriptome. Overall, the Bellerophon pipeline was able to remove between 40% and 91.9% of the chimeras in transcriptome assemblies and removed more chimeric than nonchimeric contigs. Thus, the Bellerophon sequence of filtration steps is a broadly applicable solution to improve transcriptome assemblies.
Keywords: chimera; transcriptome filtering; transcriptome quality assessment.
© 2019 The Authors. Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Frenkel‐Morgenstern, M. , Gorohovski, A. , Lacroix, V. , Rogers, M. , Ibanez, K. , Boullosa, C. , … Valencia, A. (2012). ChiTaRS: A database of human, mouse and fruit fly chimeric transcripts and RNA‐sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(D1), D142–D151. 10.1093/nar/gks1041 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

