The Prevention of Contrast Induced Nephropathy by Sarpogrelate: a Prospective Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
- PMID: 31625293
- PMCID: PMC6801223
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e261
The Prevention of Contrast Induced Nephropathy by Sarpogrelate: a Prospective Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: Although some strategies are used for prophylaxis of contrast induced nephropathy, their efficacy is not fully established. Sarpogrelate can relieve vasospasm and have anti-inflammatory action. This study examined whether sarpogrelate reduces the incidence of contrast induced nephropathy (CIN) or subsequent renal impairment during four weeks after coronary angiography compared with a control group.
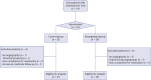
Methods: Seventy-four participants with chronic renal failure were randomly assigned to the sarpogrelate or control group. Patients assigned to the sarpogrelate group received oral saporogelate from 24 hours before contrast exposure up to one month after contrast exposure. The primary outcome of this study was the incidence of CIN within 48 hours after exposure to the contrast agent.
Results: Thirty-one subjects in the control group and 35 subjects in the sarpogrelate group were used for the analysis. Cumulative CIN occurred numerically more at 48 hours in the sarpogrelate group and less at one month without statistical significance (11.4% vs. 6.5% at 48 hours and 11.4% vs. 16.1% at one month, respectively). Baseline renal function was similar in both groups, but the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was lower in the sarpogrelate group at 12 and 48 hours compared with the control group (45.6 vs. 54.7 mL/min/1.73m²; P = 0.023 and 39.9 vs. 50.6 mL/min/1.73m²; P = 0.020, respectively). At one month, the eGFR became comparable between the two groups because the eGFR was aggravated in the control group and maintained in the sarpogrelate group.
Conclusion: This study failed to demonstrate that sarpogrelate has a renoprotective effect against contrast induced acute kidney injury.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01165567.
Keywords: Contrast Nephropathy; Coronary Angiography; Renal Insufficiency; Sarpogrelate; Serotonin.
© 2019 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Weisbord SD, Chen H, Stone RA, Kip KE, Fine MJ, Saul MI, et al. Associations of increases in serum creatinine with mortality and length of hospital stay after coronary angiography. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(10):2871–2877. - PubMed
-
- Solomon R. Contrast-medium-induced acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1998;53(1):230–242. - PubMed
-
- Mehran R, Nikolsky E. Contrast-induced nephropathy: definition, epidemiology, and patients at risk. Kidney Int Suppl. 2006;69(100):S11–5. - PubMed
-
- McCullough PA, Adam A, Becker CR, Davidson C, Lameire N, Stacul F, et al. Risk prediction of contrast-induced nephropathy. Am J Cardiol. 2006;98(6A):27K–36K. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

