Foodborne viral outbreaks associated with frozen produce
- PMID: 31625499
- PMCID: PMC6813648
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268819001791
Foodborne viral outbreaks associated with frozen produce
Abstract
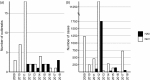
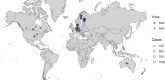
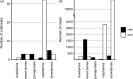
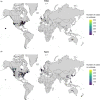
Over the past decade, frozen fruits have been a major vehicle of foodborne illnesses mainly attributed to norovirus (NoV) and hepatitis A virus (HAV) infections. Fresh produce may acquire viral contamination by direct contact with contaminated surface, water or hands, and is then frozen without undergoing proper decontamination. Due to their structural integrity, foodborne viruses are able to withstand hostile conditions such as desiccation and freezing, and endure for a long period of time without losing their infectivity. Additionally, these foods are often consumed raw or undercooked, which increases the risk of infection. Herein, we searched published literature and databases of reported outbreaks as well as the databases of news articles for the viral outbreaks associated with the consumption of frozen produce between January 2008 and December 2018; recorded the worldwide distribution of these outbreaks; and analysed the implication of consumption of different types of contaminated frozen food. In addition, we have briefly discussed the factors that contribute to an increased risk of foodborne viral infection following the consumption of frozen produce. Our results revealed that frozen fruits, especially berries and pomegranate arils, contributed to the majority of the outbreaks, and that most outbreaks were reported in industrialised countries.
Keywords: Frozen fruit; Hepatitis A virus; Norovirus; Outbreak.
Figures
References
-
- FAO (2018). Available at http://wwwfaoorg/docrep/008/y5979e/y5979e03htm.
-
- Collier MG et al. (2014) Outbreak of hepatitis A in the USA associated with frozen pomegranate arils imported from Turkey: an epidemiological case study. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 14, 976–981. - PubMed
-
- Tavoschi L et al. (2015) Food-borne diseases associated with frozen berries consumption: a historical perspective, European Union, 1983 to 2013. Euro Surveillance: Bulletin Europeen sur les Maladies Transmissibles = European Communicable Disease Bulletin 20, 21193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

