Transcriptional Profiling of the Murine Airway Response to Acute Ozone Exposure
- PMID: 31626304
- PMCID: PMC6944221
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz219
Transcriptional Profiling of the Murine Airway Response to Acute Ozone Exposure
Abstract
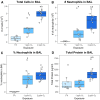
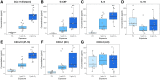
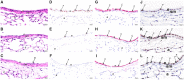
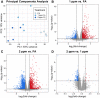
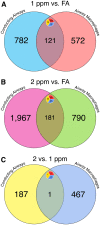
Ambient ozone (O3) exposure has serious consequences on respiratory health, including airway inflammation and injury. Decades of research have yielded thorough descriptions of these outcomes; however, less is known about the molecular processes that drive them. The aim of this study was to further describe the cellular and molecular responses to O3 exposure in murine airways, with a particular focus on transcriptional responses in 2 critical pulmonary tissue compartments: conducting airways (CA) and airway macrophages (AM). After exposing adult, female C57BL/6J mice to filtered air, 1 or 2 ppm O3, we assessed hallmark responses including airway inflammation (cell counts and cytokine secretion) and injury (epithelial permeability), followed by gene expression profiling of CA and AM by RNA-seq. As expected, we observed concentration-dependent increases in airway inflammation and injury. Conducting airways and AM both exhibited changes in gene expression to both 1 and 2 ppm O3 that were largely compartment-specific. In CA, genes associated with epithelial barrier function, detoxification processes, and cellular proliferation were altered, while O3 affected genes involved in innate immune signaling, cytokine production, and extracellular matrix remodeling in AM. Further, CA and AM also exhibited notable differences in concentration-response expression patterns for large numbers of genes. Overall, our study has described transcriptional responses to acute O3 exposure, revealing both shared and unique gene expression patterns across multiple concentrations of O3 and in 2 important O3-responsive tissues. These profiles provide broad mechanistic insight into pulmonary O3 toxicity, and reveal a variety of targets for focused follow-up studies.
Keywords: air pollution; inflammation; injury; lung; mouse; ozone; transcriptomics.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Akinbami L. J., Lynch C. D., Parker J. D., Woodruff T. J. (2010). The association between childhood asthma prevalence and monitored air pollutants in metropolitan areas, united states, 2001-2004. Environ. Res. 110, 294–301. - PubMed
-
- Anenberg S. C., Henze Daven K., Tinney V., Kinney P. L., Raich W., Fann N., Malley C. S., Roman H., Lamsal L., Duncan B., et al. (2018). Estimates of the global burden of ambient pm2.5, ozone, and no2 on asthma incidence and emergency room visits. Environ. Health Perspect. 126, 107004.. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aris R. M., Christian D., Hearne P. Q., Kerr K., Finkbeiner W. E., Balmes J. R. (1993). Ozone-induced airway inflammation in human subjects as determined by airway lavage and biopsy. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 148, 1363–1372. - PubMed
-
- Arredouani M. S., Franco F., Imrich A., Fedulov A., Lu X., Perkins D., Soininen R., Tryggvason K., Shapiro S. D., Kobzik L. (2007). Scavenger receptors SR-AI/II and MARCO limit pulmonary dendritic cell migration and allergic airway inflammation. J. Immunol. 178, 5912–5920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

