Practical Synthesis of Cap-4 RNA
- PMID: 31626389
- PMCID: PMC7004131
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201900590
Practical Synthesis of Cap-4 RNA
Abstract
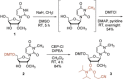
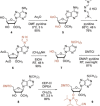
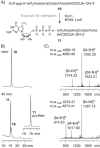
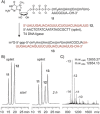
Eukaryotic mRNAs possess 5' caps that are determinants for their function. A structural characteristic of 5' caps is methylation, with this feature already present in early eukaryotes such as Trypanosoma. While the common cap-0 (m7 GpppN) shows a rather simple methylation pattern, the Trypanosoma cap-4 displays seven distinguished additional methylations within the first four nucleotides. The study of essential biological functions mediated by these unique structural features of the cap-4 and thereby of the metabolism of an important class of human pathogenic parasites is hindered by the lack of reliable preparation methods. Herein we describe the synthesis of custom-made nucleoside phosphoramidite building blocks for m62 Am and m3 Um, their incorporation into short RNAs, the efficient construction of the 5'-to-5' triphosphate bridge to guanosine by using a solid-phase approach, the selective enzymatic methylation at position N7 of the inverted guanosine, and enzymatic ligation to generate trypanosomatid mRNAs of up to 40 nucleotides in length. This study introduces a reliable synthetic strategy to the much-needed cap-4 RNA probes for integrated structural biology studies, using a combination of chemical and enzymatic steps.
Keywords: RNA modifications; chemoenzymatic synthesis; mRNA caps; oligonucleotides; solid-phase synthesis.
© 2019 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

