From Crosstalk between Immune and Bone Cells to Bone Erosion in Infection
- PMID: 31627424
- PMCID: PMC6834200
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20205154
From Crosstalk between Immune and Bone Cells to Bone Erosion in Infection
Abstract
Bone infection and inflammation leads to the infiltration of immune cells at the site of infection, where they modulate the differentiation and function of osteoclasts and osteoblasts by the secretion of various cytokines and signal mediators. In recent years, there has been a tremendous effort to understand the cells involved in these interactions and the complex pathways of signal transduction and their ultimate effect on bone metabolism. These crosstalk mechanisms between the bone and immune system finally emerged, forming a new field of research called osteoimmunology. Diseases falling into the category of osteoimmunology, such as osteoporosis, periodontitis, and bone infections are considered to have a significant implication in mortality and morbidity of patients, along with affecting their quality of life. There is a much-needed research focus in this new field, as the reported data on the immunomodulation of immune cells and their signaling pathways seems to have promising therapeutic benefits for patients.
Keywords: T cells; bone erosion; bone infection; bone remodeling; osteoclasts; signaling crosstalk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
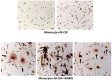
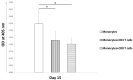
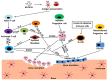
 Stimulation;
Stimulation;  Inhibition.
Inhibition.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

