A clinicohaematological prognostic model for nasal-type natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: A multicenter study
- PMID: 31628410
- PMCID: PMC6802199
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-51522-0
A clinicohaematological prognostic model for nasal-type natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: A multicenter study
Abstract
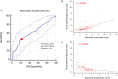
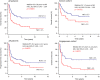
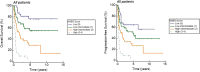
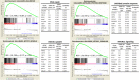
Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (NKTL) is an aggressive type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma closely associated with Epstein-Barr virus and characterized by varying degrees of systemic inflammation. We aim to examine the prognostic significance of peripheral blood neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in patients with NKTL. Therefore, we conducted a retrospective review of 178 patients with biopsy-proven NKTL from the National Cancer Centre Singapore and Samsung Medical Center, South Korea. Using receiver operating curve analysis, an optimal cut-off for high NLR (>3.5) in predicting overall survival (OS) was derived. Survival analysis was performed using the Kaplan-Meier method and multivariable Cox proportional regression. In patients with high NLR, estimated 5-year OS was 25% compared to 53% in those with low NLR. In multivariable analysis, high NLR, in addition to age ≥60 years, presence of B-symptoms and stage III/IV at diagnosis, was independently correlated with worse OS (HR 2.08; 95% CI 1.36 to 3.18; p = 0.0008) and progression-free survival (HR 1.66; 95% CI 1.11 to 2.46; p = 0.0128). A new prognostic index (NABS score) derived from these factors stratified patients into low (0), low-intermediate (1), high-intermediate (2) and high (3-4) risk subgroups, which were associated with 5-year OS of 76.5%, 55.7%, 29.2% and 0% respectively. In conclusion, high NLR is an independent prognostic marker and the NABS model can be used to risk-stratify NKTL patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Pongpruttipan T, et al. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, includes cases of natural killer cell and alphabeta, gammadelta, and alphabeta/gammadelta T-cell origin: a comprehensive clinicopathologic and phenotypic study. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:481–499. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31824433d8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

