A luciferase lysis assay reveals in vivo malignant cell sensitization by phosphoantigen prodrugs
- PMID: 31628909
- PMCID: PMC6910714
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113668
A luciferase lysis assay reveals in vivo malignant cell sensitization by phosphoantigen prodrugs
Abstract
Human Vγ9Vδ2 T cells respond to small phosphorus-containing compounds, often called phosphoantigens, which are now known to be intracellular ligands of the immune receptor butyrophilin 3A1 (BTN3A1). In order to compare the efficiency of butyrophilin ligands, we developed a luciferase-based lysis assay that measures the direct cytolysis by Vγ9Vδ2 T cells of luciferase-expressing K562 leukemia cells sensitized by phosphoantigen prodrugs. Our results show that the luciferase-based lysis assay allows in vitro and in vivo assessment of phosphoantigen activity in a way that does not require the extensive processing of flow cytometry or ELISA based approaches. In cellular assays, the structure activity relationships of phosphoantigen prodrugs correlate with ELISA-based activation assays, though phosphoantigen induced target cell lysis occurs at lower concentrations relative to T cell interferon γ production measured by ELISA. In mice dosed with phosphoantigens, a racemic aryl phosphonamidate prodrug, methyl 2-[[[(E)-5-hydroxy-4-methyl-pent-3-enyl]-(1-naphthyloxy)phosphoryl]amino]acetate (1-Nap/GlyOMe C-HMBP, 5), sensitized subcutaneous K562 tumors within minutes, and this effect was maintained at least four hours after treatment. In vivo activity of compound 5 was stronger than that of an equivalent dose of zoledronate. This luciferase lysis assay can be used for evaluation of phosphoantigens due to its time efficiency, high sensitivity, and in vivo compatibility and demonstrates rapid in vitro and in vivo sensitization of tumor cells by phosphoantigen prodrugs.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


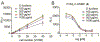


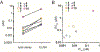

References
-
- Chien YH, Meyer C, Bonneville M, γδ T cells: first line of defense and beyond, Annu. Rev. Immunol. 32 (1) (2014) 121–55. - PubMed
-
- Vermijlen D, Gatti D, Kouzeli A, Rus T, Eberl M, γδ T cell responses: How many ligands will it take till we know?, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 84 (2018) 75–86. - PubMed
-
- Sicard H, Ingoure S, Luciani B, Serraz C, Fournie JJ, Bonneville M, et al., In vivo immunomanipulation of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells with a synthetic phosphoantigen in a preclinical nonhuman primate model, J. Immunol. 175 (8) (2005) 5471–80. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka Y, Morita CT, Tanaka Y, Nieves E, Brenner MB, Bloom BR, Natural and synthetic non-peptide antigens recognized by human γδ T cells, Nature 375 (6527) (1995) 155–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

