Coronary artery stenosis-related perfusion ratio using dynamic computed tomography myocardial perfusion imaging: a pilot for identification of hemodynamically significant coronary artery disease
- PMID: 31630340
- PMCID: PMC7497437
- DOI: 10.1007/s12928-019-00627-4
Coronary artery stenosis-related perfusion ratio using dynamic computed tomography myocardial perfusion imaging: a pilot for identification of hemodynamically significant coronary artery disease
Abstract
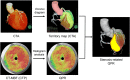
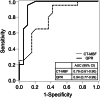
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of the stenosis-related quantitative perfusion ratio (QPR) for detecting hemodynamically significant coronary artery disease (CAD). Twenty-seven patients were retrospectively enrolled. All patients underwent dynamic myocardial computed tomography perfusion (CTP) and coronary computed tomography angiography (CTA) before invasive coronary angiography (ICA) measuring the fractional flow reserve (FFR). Coronary lesions with FFR ≤ 0.8 were defined as hemodynamically significant CAD. The myocardial blood flow (MBF) was calculated using dynamic CTP data, and CT-QPR was calculated as the CT-MBF relative to the reference CT-MBF. The stenosis-related CT-MBF and QPR were calculated using Voronoi diagram-based myocardial segmentation from coronary CTA data. The relationships between FFR and stenosis-related CT-MBF or QPR and the diagnostic performance of the stenosis-related CT-MBF and QPR were evaluated. Of 81 vessels, FFR was measured in 39 vessels, and 20 vessels (51%) in 15 patients were diagnosed as hemodynamically significant CAD. The stenosis-related CT-QPR showed better correlation (r = 0.70, p < 0.05) than CT-MBF (r = 0.56, p < 0.05). Sensitivity and specificity for detecting hemodynamically significant CAD were 95% and 58% for CT-MBF, and 95% and 90% for CT-QPR, respectively. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for the CT-QPR was significantly higher than that for the CT-MBF (0.94 vs. 0.79; p < 0.05). The stenosis-related CT-QPR derived from dynamic myocardial CTP and coronary CTA showed a better correlation with FFR and a higher diagnostic performance for detecting hemodynamically significant CAD than the stenosis-related CT-MBF.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Coronary artery disease; Fractional flow reserve; Myocardial blood flow; Myocardial ischemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Montalescot G, Sechtem U, Achenbach S, Andreotti F, Arden C, Budaj A, et al. 2013 ESC guidelines on the management of stable coronary artery disease: the Task Force on the management of stable coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2949–3003. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht296. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Celeng C, Leiner T, Maurovich-Horvat P, Merkely B, de Jong P, Dankbaar JW, et al. Anatomical and functional computed tomography for diagnosing hemodynamically significant coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;12:1316–1325. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.07.022. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

