Sphingolipid Modulation Activates Proteostasis Programs to Govern Human Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal
- PMID: 31631013
- PMCID: PMC6838675
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.09.008
Sphingolipid Modulation Activates Proteostasis Programs to Govern Human Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal
Abstract
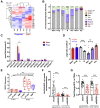
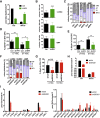
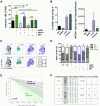
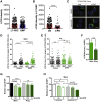
Cellular stress responses serve as crucial decision points balancing persistence or culling of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) for lifelong blood production. Although strong stressors cull HSCs, the linkage between stress programs and self-renewal properties that underlie human HSC maintenance remains unknown, particularly at quiescence exit when HSCs must also dynamically shift metabolic state. Here, we demonstrate distinct wiring of the sphingolipidome across the human hematopoietic hierarchy and find that genetic or pharmacologic modulation of the sphingolipid enzyme DEGS1 regulates lineage differentiation. Inhibition of DEGS1 in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells during the transition from quiescence to cellular activation with N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide activates coordinated stress pathways that coalesce on endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy programs to maintain immunophenotypic and functional HSCs. Thus, our work identifies a linkage between sphingolipid metabolism, proteostatic quality control systems, and HSC self-renewal and provides therapeutic targets for improving HSC-based cellular therapeutics.
Keywords: DEGS1; StemRegenin-1; UM171; autophagy; fenretinide; hematopoietic stem cell; lipidomics; sphingolipid metabolism; umbilical cord blood; unfolded protein response.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare a patent titled “4HPR and its use in the culturing of hematopoietic stem cells” no. PCT/CA2017/000107 filed May 3, 2017 related to this work.
Figures




Comment in
-
Evaluation of Xie et al.: Sphingolipid Modulation Activates Proteostasis Programs to Govern Human Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal.Cell Stem Cell. 2019 Nov 7;25(5):585-586. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.10.009. Cell Stem Cell. 2019. PMID: 31703766
References
-
- Amirache F., Lévy C., Costa C., Mangeot P.E., Torbett B.E., Wang C.X., Nègre D., Cosset F.L., Verhoeyen E. Mystery solved: VSV-G-LVs do not allow efficient gene transfer into unstimulated T cells, B cells, and HSCs because they lack the LDL receptor. Blood. 2014;123:1422–1424. - PubMed
-
- Bielawski J., Pierce J.S., Snider J., Rembiesa B., Szulc Z.M., Bielawska A. Comprehensive quantitative analysis of bioactive sphingolipids by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009;579:443–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

