Predictive Factors And Long-Term Visual Outcomes After Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment Of Retinal Angiomatous Proliferation
- PMID: 31631966
- PMCID: PMC6790115
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S224319
Predictive Factors And Long-Term Visual Outcomes After Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment Of Retinal Angiomatous Proliferation
Abstract
Purpose: To report the results of 9-year follow-up examinations and predictive factors for visual acuity outcome after intravitreal injection of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agents to treat retinal angiomatous proliferation (RAP).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective observational study of 85 treatment-naïve eyes in 61 patients (21 men, 40 women; age range, 70-95 years; mean age, 84.0 years) treated with intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF agents. All patients received three consecutive monthly injections as an induction treatment. During the maintenance phase, the patients received intravitreal injections as needed or fixed dosing. The primary outcome measures were best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) during the follow-up period. Furthermore, we investigated potential predictive factors of improvement in visual acuity. The proportion of patients who developed specific complications were also analyzed.
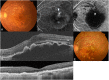
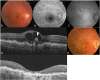
Results: The mean BCVA gradually decreased from 0.58 at baseline to 0.70 at 36 months (P = 0.146), 0.82 at 48 months (P = 0.004), and 0.92 at 108 months (P = 0.021). Improvement in visual acuity at the final visits was associated with baseline visual acuity and central foveal thickness. Massive subretinal hemorrhage, fibrotic scars, and macular atrophy developed in 4 (4.7%), 9 (10.6%), and 50 (56.8%) eyes, respectively, at the final visits, and were all significantly associated with final visual acuity (P = 0.013, P < 0.001, and P = 0.001, respectively).
Conclusion: Long-term stabilization of vision in patients with RAP, regardless of treatment modality, was difficult to achieve by using intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF agents. Earlier detection and treatment are important to maintain visual acuity in patients with RAP.
Keywords: aflibercept; age-related macular degeneration; intravitreal injection; ranibizumab; retinal angiomatous proliferation.
© 2019 Maruyama-Inoue et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monotherapy or combined with verteporfin photodynamic therapy for retinal angiomatous proliferation: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 12;14:1141077. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1141077. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37377929 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term visual outcome and prognostic factors of Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment for retinal angiomatous proliferation.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016 Jan;254(1):23-30. doi: 10.1007/s00417-015-2993-3. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 25825231
-
Long-term results of intravitreal ranibizumab for the treatment of retinal angiomatous proliferation and utility of an advanced RPE analysis performed using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography.Br J Ophthalmol. 2014 Jul;98(7):956-60. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2013-304251. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Br J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24599418
-
Intravitreal ranibizumab (Lucentis) in the treatment of retinal angiomatous proliferation (RAP).Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009 Sep;247(9):1165-71. doi: 10.1007/s00417-009-1089-3. Epub 2009 Apr 29. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19404661
-
Clinical evidence of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide in the management of age-related macular degeneration.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Feb;12(2):149-72. doi: 10.2174/138945011794182746. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 20887246 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monotherapy or combined with verteporfin photodynamic therapy for retinal angiomatous proliferation: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 12;14:1141077. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1141077. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37377929 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes and the association between early detection of retinal pigment epithelial atrophy and remission after loading dose in eyes with retinal angiomatous proliferation.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul;69(4):504-511. doi: 10.1007/s10384-025-01189-0. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40202693
-
Seven-year outcome after 1-year fixed regimen of intravitreal aflibercept injections followed by pro re nata treatment for neovascular age-related macular degeneration.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023 Jul;261(7):1871-1881. doi: 10.1007/s00417-023-05982-w. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36735070
References
-
- Johnson TM, Glaser BM. Focal laser ablation of retinal angiomatous proliferation. Retina. 2006;26:765–772. doi:10.1097/01.iae.0000244264.98642.af - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

