Aucubin Protects Chondrocytes Against IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis In Vitro And Inhibits Osteoarthritis In Mice Model
- PMID: 31631977
- PMCID: PMC6791845
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S210220
Aucubin Protects Chondrocytes Against IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis In Vitro And Inhibits Osteoarthritis In Mice Model
Abstract
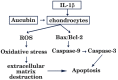
Objective: Chondrocyte apoptosis has also been strongly correlated with the severity of cartilage damage and matrix depletion in an osteoarthritis (OA) joint. Therefore, pharmacological inhibitors of apoptosis may provide a novel treatment option for patients with OA. Aucubin, a natural compound isolated from Eucommia ulmoides, has been proved to possess antioxidative and anti-apoptotic properties. However, anti-osteoarthritis effect of aucubin in animal model and anti-apoptotic response of aucubin in OA chondrocytes remain unclear. This study aimed to determine whether aucubin could slow progression of OA in a mouse model and inhibit the IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis.
Methods: OA severity and articular cartilage degradation were evaluated by Safranin-O staining, Hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining, and Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) standards. Chondrocyte viability was observed by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) and live/dead cells assay; the apoptotic rate of chondrocytes was evaluated by flow cytometry (FCM) with Annexin V-FITC/PI kit. Mediators of apoptosis were tested by Western blot of Bax, caspase-3, caspase-9, and Bcl-2 expression. The intracellular levels of Reactive oxygen species (ROS) were assessed by the probe of 2,7-Dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCFH-DA).
Results: The articular cartilage in the limb with destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) exhibited early OA-like manifestations characterized by proteoglycan loss, cartilage fibrillation, and erosion, with lower OARSI score. Oral administration of aucubin remarkably attenuated the loss of proteoglycan and the articular cartilage erosion and decreased the OARSI scores underwent DMM surgery. Aucubin treatment significantly reverses IL-1β-induced cytotoxicity and attenuated the IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis. In addition, aucubin can significantly inhibit mediators of apoptosis in rat primary chondrocytes. Furthermore, aucubin remarkably attenuated the IL-1β-induced intracellular ROS production.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that aucubin has a protective effect on articular cartilage and slowing progression of OA in a mouse model. This protective effect may result from inhibiting chondrocyte apoptosis and excessive ROS production.
Keywords: IL-1β; ROS; apoptosis; aucubin; osteoarthritis.
© 2019 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
-
- Mistry D, Oue Y, Chambers MG, Kayser MV, Mason RM. Chondrocyte death during murine osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12(2):131–141. - PubMed
-
- Musumeci G, Loreto C, Carnazza ML, Strehin I, Elisseeff J. OA cartilage derived chondrocytes encapsulated in poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) for the evaluation of cartilage restoration and apoptosis in an in vitro model. Histol Histopathol. 2011;26(10):1265–1278. doi:10.14670/HH-26.1265 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

