Characterization of phenotypic and genotypic traits of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates recovered from a tertiary care hospital in Taif, Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 31632100
- PMCID: PMC6781848
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S206691
Characterization of phenotypic and genotypic traits of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates recovered from a tertiary care hospital in Taif, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background and objective: Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) is a common nosocomial pathogen, which developed multi-drug-resistance to different classes of antibiotics including carbapenems. This study examined ten common carbapenemase genes among 32 carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii clinical isolates recovered from Taif, Saudi Arabia.
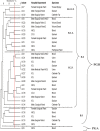
Methods: Isolates were phenotypically identified to the genus level by Vitek®2 and API 20NE®. The species level was confirmed by the amplification of bla OXA-51. The susceptibility for 21 different antibiotics was performed by Vitek 2 and modified Kirby-Bauer method. Isolates were genetically screened for 10 carbapenemases. Phylogenetic relatedness between isolates was determined by ERIC-PCR.
Results: Genotypically identified A. baumannii represented 100% of the total phenotypically identified Acinetobacter spp. All the carbapenem-resistant isolates were sensitive to polymyxin B and colistin. Among the other antibiotics, ampicillin/sulbactam and tigecycline were the most effective agents. 90.8% of the isolates were resistant to all ten investigated β-lactams. bla OXA-51, bla IPM, bla NDM and bla OXA-23 were detected in 100%, 87.5%, 62.5% and 59.4% of isolates, respectively. Also, bla VIM and bla OXA-40 were less prevalent and were detected in 9.3% and 3.1% of the isolates, respectively. In addition, bla KPC, bla OXA-48, bla OXA-58, bla OXA-181 were not detected in any isolate. The A. baumannii isolates were categorised into ten genotypes on the basis of the detected carbapenemase genes and ERIC-PCR revealed a remarkable clonal diversity among these isolates.
Conclusion: Class A and class D carbapenemase genes were the most commonly detected among carbapenem resistant A. baumannii (CRAB) clinical isolates.
Keywords: A. baumannii; ERIC-PCR; blaOXA-51; carbapenemases; carbapenems.
© 2019 El-Badawy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Majid Bouzari D, Abedini F, Yadegari S. Identification of genomic species of Acinetobacter isolated from burns of ICU patients. Arch Iran Med. 2015;18(10):638–642. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous