Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31632337
- PMCID: PMC6779767
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.01043
Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
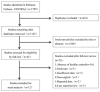
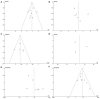
Objective: The objective of our study was to investigate the potential association between the occurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) and saccular dysfunction using cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (cVEMP) testing. Methods: The databases including Pubmed, Embase, and CENTRAL were systemically searched for case-control literatures investigating saccular dysfunction using cVEMP testing in BPPV patients compared with healthy controls. The literatures were published up to 16 April 2019 and were limited to the English language. All statistical processes were carried out using software Review Manager, version 5.3. Subgroup analysis and sensitive analysis were performed simultaneously. Results: Of the 12 case-control studies confirmed for meta-analysis, p13 latency of cVEMP was assessed in 8 studies, n23 latency in 6 studies, amplitude in 5 studies, asymmetry ratio (AR) in 3 studies, proportion of absent response in 9 studies, and abnormal cVEMP in 8 studies. Compared with healthy controls, the p13 mean latency of cVEMP was longer (MD = 0.88, 95% CI = 0.64-1.12, p < 0.00001), the mean amplitude was lower (SMD = -0.60, 95% CI = -0.80 to -0.41, p < 0.00001), and the proportions of absent response (OR = 8.76, 95% CI = 2.28-33.61, p = 0.002), and abnormal cVEMP (OR = 7.47, 95% CI = 4.65-12.01, p < 0.00001) were higher in BPPV patients. But there was no significant difference in the n23 mean latency (MD = 0.37, 95% CI = -0.23-0.98, p = 0.22) and the AR of cVEMP (MD = 3.95, 95% CI = -4.75-12.65, p = 0.37) between BPPV patients and healthy controls. In the sub-group analysis based on age, only the result of the proportion of absent response of cVEMP indicated a significant difference existed (p = 0.002) between the studies with age-matched controls (OR = 2.78, 95% CI = 1.09-7.10, p = 0.03) and the studies without age-matched controls (OR = 53.85, 95% CI = 10.09-287.13, p < 0.00001). In the sub-group analysis of the proportion of abnormal cVEMP according to the diagnostic criteria of abnormal cVEMP, the result indicated no significant difference existed between the four groups (p = 0.61, I 2 = 0%). In the sensitivity analysis, we obtained the consistent results after removing each study sequentially. Conclusion: The meta-analysis reveals that saccular dysfunction may be associated with BPPV occurrence, and neural degeneration in the saccular macula may be a potential pathogenesis for BPPV.
Keywords: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potentials; meta-analysis; saccule; systematic review.
Copyright © 2019 Chen, Yu, Li, Zhao, Dai and Wang.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Ocular vs. Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Neurol. 2020 Oct 26;11:596454. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.596454. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33193065 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of cervical and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Dec;276(12):3257-3265. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05674-4. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 31605189 Review.
-
Efficacy of cervical and ocular vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in evaluation of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of posterior semicircular canal.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Sep;273(9):2523-32. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3867-3. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26718546
-
[Primary benign paroxysmal positional vertigo vestibular detection of evoked myogenic potential significance].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;28(16):1215-8. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25464560 Chinese.
-
Clinical and Prognostic Implications of Cervical and Ocular Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (cVEMP and oVEMP) in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV): A Prospective Study.Audiol Res. 2023 Sep 12;13(5):700-709. doi: 10.3390/audiolres13050061. Audiol Res. 2023. PMID: 37736942 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bilateral Dysfunction of Otolith Pathway in Patients With Unilateral Idiopathic BPPV Detected by ACS-VEMPs.Front Neurol. 2022 Aug 26;13:921133. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.921133. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36090849 Free PMC article.
-
Vestibular syncope: clinical characteristics and mechanism.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2022 Oct;9(10):1616-1625. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51661. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36056529 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular vs. Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Neurol. 2020 Oct 26;11:596454. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.596454. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33193065 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

