Oxymatrine inhibits the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by reducing the activity of MMP-2/-9 via regulating p38 signaling pathway
- PMID: 31632484
- PMCID: PMC6775708
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.32875
Oxymatrine inhibits the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by reducing the activity of MMP-2/-9 via regulating p38 signaling pathway
Abstract
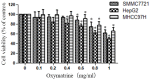
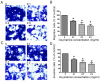
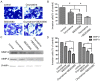
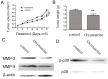
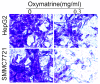
As one of the major alkaloid components in Sophoraflavescensait (kushen), oxymatrine has been used widely across the world in anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer therapies. However, the effect in the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and related mechanism(s) are still unclear. The present study aimed to investigate the anti-metastatic effect of oxymatrine on HCC cells. Oxymatrine could also inhibit the protein levels of MMP-2/-9 in a dose-dependent relationship. Moreover, oxymatrine reduces the activity of p38 signaling pathway via inhibiting the phosphorylation of p38. The inhibition effect of oxymatrine on the expression of MMP-2/-9 and the phosphorylated of p38 was also detected in vivo. Combined treatment with p38 signaling pathway inhibitor and oxymatrine may have a synergistic effect on MMP-2/-9 and invasion of HCC cells. Therefore, oxymatrine may have inhibited GBC invasiveness by reducing the expression of MMP-2/-9 via inhibiting the activity of p38 signaling pathway. As a potentially novel therapeutic drug, oxymatrine may play an important role in the treatment of HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; matrix metalloproteinase; migration and invasion; oxymatrine; p38 signaling pathway.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Chen J, Xu X, Ling Q. et al. Role of Pittsburgh modified TNM criteria in prognosis prediction of liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Chinese medical journal. 2007;120:2200–3. - PubMed
-
- Gialeli C, Theocharis AD, Karamanos NK. Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 2011;278:16–27. - PubMed
-
- Wang SN, Lee KT, Tsai CJ. et al. Phosphorylated p38 and JNK MAPK proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma. European journal of clinical investigation. 2012;42:1295–301. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

