The combination of preoperative fibrinogen and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio is a predictive prognostic factor in esophagogastric junction and upper gastric cancer
- PMID: 31632495
- PMCID: PMC6775700
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.31162
The combination of preoperative fibrinogen and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio is a predictive prognostic factor in esophagogastric junction and upper gastric cancer
Abstract
Objective: Cancer-associated systemic inflammation response and hyperfibrinogenemia play crucial roles in cancer progression and prognosis. In this study, we assessed the clinical value of the preoperative fibrinogen and the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction (AEG) and upper gastric cancer (UGC). Methods: Patients with AEG or UGC who underwent curative surgery were divided into a training set (n=161) and a validation set (n=195). Univariate and multivariate Cox analyses were performed to evaluate the prognostic indicators for overall survival (OS). The optimization cut-off values for fibrinogen and the NLR were 3.09g/L and 1.84, respectively. The combination of fibrinogen and NLR (F-NLR) was 2 for patients with high fibrinogen (≥3.09g/L) and elevated NLR (≥1.84), whereas those with one or neither were indexed as 1 or 0, respectively. Results: F-NLR was identified as an independent prognostic indicator for OS in the training set (P=0.007) which was confirmed in the validation set (P=0.003). In the subgroup analyses, the prognostic significance of F-NLR was still maintained for stages I-II (P = 0.030 in the training set; and P =0.020 in the validation set) and III (P = 0.001 in the training set; and P <0.001 in the validation set).Notably, among patients with F-NLR 2 could benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy compared with those with F-NLR 0-1 (P = 0.020 in the training set; and P =0.005 in the validation set). Conclusions: The preoperative F-NLR score is an independent prognosis indicator for patients with AEG and UGC. And it may help clinicians to identify those patients who at high prognostic risk and will benefit from planning individualized treatment strategies.
Keywords: fibrinogen; gastric cancer, adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; prognosis..
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
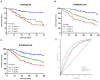
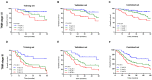
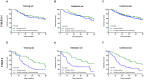
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5–29. - PubMed
-
- Siewert JR. Adenocarcinoma of the esophago-gastric junction. Gastric Cancer. 1999;2(2):87–88. - PubMed
-
- Steevens J, Botterweck AA, Dirx MJ, van den Brandt PA, Schouten LJ. Trends in incidence of oesophageal and stomach cancer subtypes in Europe. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;22(6):669–78. - PubMed
-
- Kusano C, Gotoda T, Khor CJ. et al. Changing trends in the proportion of adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction in a large tertiary referral center in Japan. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23(11):1662–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

