Neuroradiological Findings in the Spinocerebellar Ataxias
- PMID: 31632837
- PMCID: PMC6765228
- DOI: 10.7916/tohm.v0.682
Neuroradiological Findings in the Spinocerebellar Ataxias
Abstract
Background: The spinocerebellar ataxias (SCAs) are a group of autosomal dominant degenerative diseases characterized by cerebellar ataxia. Classified according to gene discovery, specific features of the SCAs - clinical, laboratorial, and neuroradiological (NR) - can facilitate establishing the diagnosis. The purpose of this study was to review the particular NR abnormalities in the main SCAs.
Methods: We conducted a literature search on this topic.
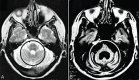
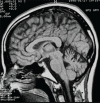
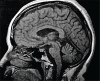
Results: The main NR characteristics of brain imaging (magnetic resonance imaging or computerized tomography) in SCAs were: (1) pure cerebellar atrophy; (2) cerebellar atrophy with other findings (e.g., pontine, olivopontocerebellar, spinal, cortical, or subcortical atrophy; "hot cross bun sign", and demyelinating lesions); (3) selective cerebellar atrophy; (4) no cerebellar atrophy.
Discussion: The main NR abnormalities in the commonest SCAs, are not pathognomonic of any specific genotype, but can be helpful in limiting the diagnostic options. We are progressing to a better understanding of the SCAs, not only genetically, but also pathologically; NR is helpful in the challenge of diagnosing the specific genotype of SCA.
Keywords: Spinocerebellar ataxia; ataxia; brain imaging; cerebellar diseases; gait ataxia; magnetic resonance imaging.
© 2019 Meira et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding: None. Conflicts of Interest: The authors report no conflicts of interest. Ethics Statement: Not applicable for this category of article.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

