Etanercept-associated Nephropathy
- PMID: 31632872
- PMCID: PMC6795349
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.5419
Etanercept-associated Nephropathy
Abstract
Anti-TNF (tumor necrosis factor) medications work by inhibiting the production of TNF or its effect on target organs. TNF is a cell-signaling protein, or cytokine, involved in systemic inflammation and is one of the cytokines that make up the acute phase reactants. TNF inhibitors are available for the treatment of a number of rheumatic and other immune-mediated diseases. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with anti-TNFα (tumor necrosis factor-alpha) agents may lead to autoantibody formation and flares of vasculitis. Although medications are a common cause of renal injury, anti-TNFα medications very rarely cause renal complications. We present a case of a patient who presented with nausea and flu-like illness and was ultimately found to have etanercept-induced nephropathy.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; anti tnf; anti-tnf therapy; etanercept; glomerulo nephritis; rheumatoid arthritis; tnf inhibitor; tnf-tumor necrosis factor; tumor necrosis factor alpha (tnf alpha).
Copyright © 2019, Ammar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
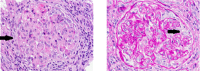
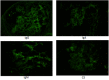
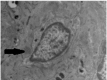
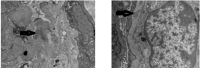
References
-
- Enbrel (etanercept) [Jul;2019 ];https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/103795s5556lbl... 1998
-
- Life-threatening hypercalcemia and acute kidney injury induced by etanercept. Tsevi YM, Aydin S, Durez P, Labriola L. Nephrol Ther. 2018;14:478–482. - PubMed
-
- Acute kidney injury due to renal sarcoidosis during etanercept therapy: a case report and literature review. Akiyama M, Kaneko Y, Hanaoka H, Kuwana M, Takeuchi T. Intern Med. 2015;54:1131–1134. - PubMed
-
- Membranous glomerulonephritis with the use of etanercept in ankylosing spondylitis. Kaushik P, Rahmani M, Ellison W. Ann Pharmacother. 2011;45:1585. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
