Trends in the Use of Medications and Supplements to Treat or Prevent Dementia: A Population-based Study
- PMID: 31633558
- PMCID: PMC7156330
- DOI: 10.1097/WAD.0000000000000357
Trends in the Use of Medications and Supplements to Treat or Prevent Dementia: A Population-based Study
Abstract
Objective: To examine older adults' use over time of agents to treat or prevent dementia or enhance memory.
Design: Longitudinal community study with 10-year annual follow-up (2006-2017).
Setting: Population-based cohort.
Participants: A total of 1982 individuals with a mean (SD) age of 77 (7.4) years at baseline.
Measurements: Demographics, self-report, direct inspection of prescription antidementia drugs and nonprescription supplements, cognitive and functional assessments, Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR®) Dementia Staging Instrument.
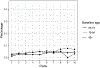
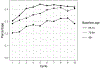
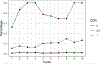
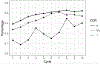
Results: Supplement use was reported by 27% to 42% of participants over 10 years. Use was associated with younger age, high school or greater education, good to excellent self-reported health, higher memory test scores, and absence of cognitive impairment or dementia (CDR=0). Over the same period, about 2% to 6% of participants took prescription dementia medications over 10 years. Use was associated with lower memory test scores, at least mild cognitive impairment (CDR≥0.5), fair to poor self-rated health, and high school or lesser education.
Conclusions: The use of both prescription drugs and supplements increased over time, except for decreases in ginkgo and vitamin E. Prescription drug use appeared in line with prescribing guidelines. Supplement use was associated with higher education and better self-rated health; it persists despite a lack of supportive evidence.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Raina P, Santaguida P, Ismaila A, et al. Effectiveness of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for treating dementia: evidence review for a clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2008; 148(5): 379–97. - PubMed
-
- Deardorff WJ, Feen E, and Grossberg GT. The Use of Cholinesterase Inhibitors Across All Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease. Drugs Aging. 2015; 32(7): 537–47. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien JT, Holmes C, Jones M, et al. Clinical practice withanti-dementia drugs: a revised (third) consensus statement from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2017; 31(2): 147–168. - PubMed
-
- Bailey RL, Gahche JJ, Miller PE, et al. Why US adults use dietary supplements. JAMA Intern Med. 2013; 173(5): 355–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

