Cytosolic Delivery of Macromolecules in Live Human Cells Using the Combined Endosomal Escape Activities of a Small Molecule and Cell Penetrating Peptides
- PMID: 31633910
- PMCID: PMC7008471
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00585
Cytosolic Delivery of Macromolecules in Live Human Cells Using the Combined Endosomal Escape Activities of a Small Molecule and Cell Penetrating Peptides
Abstract
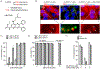
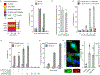
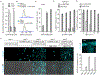
Ineffective cellular delivery is a common problem in numerous biological applications. Developing delivery reagents that work robustly in a variety of experimental settings remains a challenge. Herein, we report how peptides derived from the prototypical cell penetrating peptide TAT can be used in combination with a small molecule, UNC7938, to deliver macromolecules into the cytosol of cells by a simple co-incubation protocol. We establish successful delivery of peptides, DNA plasmids, and a single-chain variable fragment antibody. We also demonstrate that delivery works in hard-to-transfect mammalian cells and under conditions typically inhibitory to cell-penetrating peptides. Mechanistically, UNC7938 destabilizes the membrane of endosomes. This, in turn, enhances the endosome-leakage activity of cell-penetrating peptides and facilitates the endosomal escape of macromolecules initially internalized by mammalian cells via endocytosis. This combined selective membrane-destabilization represents a new chemical space for delivery tools and provides a novel solution to the problem of endosomal entrapment that often limits the effectiveness of reagent-based delivery approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
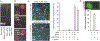
References
-
- Stewart MP et al., In vitro and ex vivo strategies for intracellular delivery. Nature 538, 183–192 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Mueller J, Kretzschmar I, Volkmer R, Boisguerin P, Comparison of Cellular Uptake Using 22 CPPs in 4 Different Cell Lines. Bioconjugate Chemistry 19, 2363–2374 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Dissanayake S, Denny WA, Gamage S, Sarojini V, Recent developments in anticancer drug delivery using cell penetrating and tumor targeting peptides. Journal of Controlled Release 250, 62–76 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Higa M et al., Identification of a novel cell-penetrating peptide targeting human glioblastoma cell lines as a cancer-homing transporter. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 457, 206–212 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

