Diurnal Regulation of Renal Electrolyte Excretion: The Role of Paracrine Factors
- PMID: 31635525
- PMCID: PMC7012674
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021119-034446
Diurnal Regulation of Renal Electrolyte Excretion: The Role of Paracrine Factors
Abstract
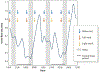
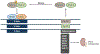
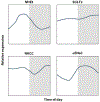
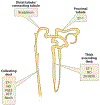
Many physiological processes, including most kidney-related functions, follow specific rhythms tied to a 24-h cycle. This is largely because circadian genes operate in virtually every cell type in the body. In addition, many noncanonical genes have intrinsic circadian rhythms, especially within the liver and kidney. This new level of complexity applies to the control of renal electrolyte excretion. Furthermore, there is growing evidence that paracrine and autocrine factors, especially the endothelin system, are regulated by clock genes. We have known for decades that excretion of electrolytes is dependent on time of day, which could play an important role in fluid volume balance and blood pressure control. Here, we review what is known about the interplay between paracrine and circadian control of electrolyte excretion. The hope is that recognition of paracrine and circadian factors can be considered more deeply in the future when integrating with well-established neuroendocrine control of excretion.
Keywords: circadian rhythms; clock genes; endothelin; potassium; purinergic receptors; sodium.
Figures


References
-
- de Bold AJ, Borenstein HB, Veress AT, Sonnenberg H. 1981. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci 28:89–94 - PubMed
-
- Praetorius HA, Leipziger J. 2010. Intrarenal purinergic signaling in the control of renal tubular transport. Annu Rev Physiol 72:377–93 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

