Reliability and accuracy of individual Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score regions using a medical and a smartphone reading system in a telestroke network
- PMID: 31635531
- PMCID: PMC8366140
- DOI: 10.1177/1357633X19881863
Reliability and accuracy of individual Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score regions using a medical and a smartphone reading system in a telestroke network
Abstract
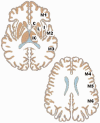
Introduction: The aim of this study was to assess individual regions of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score in noncontrast head computed tomography interpretations using a smartphone in a telestroke network, by comparison to a medical monitor.
Methods: The review board of our institution approved this retrospective study. A factorial design with 188 patients, four radiologists and two reading systems was used. Accuracy and reliability were evaluated.
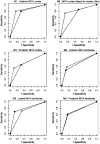
Results: Very good interobserver agreements were observed on the total Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score for both the medical and smartphone reading systems, with intraclass correlation coefficients of 0.91 and 0.84 respectively. Interobserver agreements were moderate to very good for the medical reading system (all intraclass correlation coefficients >0.74), whereas they were fair to very good for the smartphone (intraclass correlation coefficients ranged from 0.31-0.81). All intraobserver agreements were good (intraclass correlation coefficient >0.64), except for internal capsule (0.48) and M2 (0.55) regions. The areas under the receiver-operating curve ranged from 0.69-0.89 for the medical system, while for the smartphone ranged from 0.44-0.86. No statistical differences were observed between medical and smartphone reading systems for each region (all p > 0.05).
Discussion: If radiologists are better trained in the evaluation of the lesions in the insula, the internal capsule and the M2 regions, the total and the dichotomised Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score will be more precise. Hence, ruling out contraindications to thrombolysis administration will be improved, allowing assessment of head computed tomography in a telestroke network using a smartphone to be a common practice.
Keywords: Accuracy; Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score; agreement; displays; receiver-operating characteristic; reliability; smartphone; stroke; telehealth; telestroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP, Jr, et al.. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013; 44: 870–947. - PubMed
-
- Demchuk AM, Hill MD, Barber PA, et al.. Importance of early ischemic computed tomography changes using ASPECTS in NINDS rtPA Stroke Study. Stroke 2005; 36: 2110–2115. - PubMed
-
- Tan BY, Wan-Yee K, Paliwal P, et al.. Good intracranial collaterals trump poor ASPECTS (Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score) for intravenous thrombolysis in anterior circulation acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2016; 47: 2292–2298. - PubMed
-
- Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Zhang J, et al.. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. ASPECTS Study Group. Alberta Stroke Programme Early CT Score. Lancet 2000; 355: 1670–1674. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

