Expert-level detection of acute intracranial hemorrhage on head computed tomography using deep learning
- PMID: 31636195
- PMCID: PMC6842581
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1908021116
Expert-level detection of acute intracranial hemorrhage on head computed tomography using deep learning
Abstract
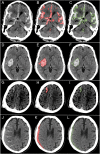
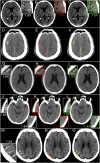
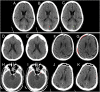
Computed tomography (CT) of the head is used worldwide to diagnose neurologic emergencies. However, expertise is required to interpret these scans, and even highly trained experts may miss subtle life-threatening findings. For head CT, a unique challenge is to identify, with perfect or near-perfect sensitivity and very high specificity, often small subtle abnormalities on a multislice cross-sectional (three-dimensional [3D]) imaging modality that is characterized by poor soft tissue contrast, low signal-to-noise using current low radiation-dose protocols, and a high incidence of artifacts. We trained a fully convolutional neural network with 4,396 head CT scans performed at the University of California at San Francisco and affiliated hospitals and compared the algorithm's performance to that of 4 American Board of Radiology (ABR) certified radiologists on an independent test set of 200 randomly selected head CT scans. Our algorithm demonstrated the highest accuracy to date for this clinical application, with a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) area under the curve (AUC) of 0.991 ± 0.006 for identification of examinations positive for acute intracranial hemorrhage, and also exceeded the performance of 2 of 4 radiologists. We demonstrate an end-to-end network that performs joint classification and segmentation with examination-level classification comparable to experts, in addition to robust localization of abnormalities, including some that are missed by radiologists, both of which are critically important elements for this application.
Keywords: deep learning; head computed tomography; intracranial hemorrhage; radiology.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: E.L.Y. and P.M. are named inventors on US Patent and Trademark Office No. 62/269, 778, “Interpretation and Quantification of Emergency Features on Head Computed Tomography” filed by the Regents of the University of California. W.K., C.H., P.M., J.M., and E.L.Y. are named inventors on a provisional patent application titled “Expert-Level Detection of Acute Intracranial Hemorrhage on Head CT scans” filed by the University of California Regents.
Figures



References
-
- Gulshan V., et al. , Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA 316, 2402–2410 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Chilamkurthy S., et al. , Deep learning algorithms for detection of critical findings in head CT scans: A retrospective study. Lancet 392, 2388–2396 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Titano J. J., et al. , Automated deep-neural-network surveillance of cranial images for acute neurologic events. Nat. Med. 24, 1337–1341 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

