Sialadenoma papilliferum: Bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 31636877
- PMCID: PMC6797451
- DOI: 10.4317/jced.56055
Sialadenoma papilliferum: Bibliometric analysis
Abstract
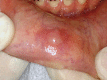
Background: Sialadenoma papilliferum is a benign rare condition of salivary glands showing a characteristic papillary growth of the ductal epithelium that ends up being confused with more frequent lesions of the oral cavity. Objectives: To perform a bibliometric analysis of all articles about Sialadenoma papilliferum in the oral cavity and to add a singular case report of Sialadenoma in the lower lip.
Material and methods: A total of 36 publications referring to Sialadenoma papilliferum in the oral cavity from the PubMed platform was reviewed. The specific data were collected, and a bibliometric analysis was performed using Microsoft Excel. The results obtained were then compared with this new case report.
Results: The people most affected with sialadenoma were white males at the average age of 56. The lesion was asymptomatic, usually white or red, with an average size of 1.4 cm, and the palate was by far the most affected site. The majority of the lesions were excised, and only two cases indicated recurrence.
Conclusions: With surgical removal, Sialadenoma papilliferum has a favorable prognosis and no further treatment is required. Due to few recorded cases of recurrence, a long follow-up period is recommended to ensure that the lesion does not redevelop. Key words:Sialadenoma papilliferum, salivary gland, oral cavity, bibliometric analysis.
Copyright: © 2019 Medicina Oral S.L.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement:Antonio Jorge Araújo de Vasconcelos II declares that he has no conflict of interest. Luana Rafaela Gerber declares that she has no conflict of interest. Stanny Hagath Maciel Saraiva declares that she has no conflict of interest. Pâmela Oliveira de Vasconcelos declares that she has no conflict of interest. Lioney Nobre Cabral declares that he has no conflict of interest. Tiago Novaes Pinheiro declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abrams AM, Finck FM. Sialadenoma papilliferum: a previously unreported salivary gland tumor. Cancer. 1969;5:1057–63. - PubMed
-
- Kubota Y, Kubo C, Mori Y. Sialadenoma papilliferum of the hard palate: a case report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;70:1609–12. - PubMed
-
- Maiorano E, Favia G, Ricco R. Sialadenoma papilliferum: an immunohistochemical study of five cases. J Oral Pathol Med. 1996;25:336–42. - PubMed
-
- van der Wal JE, van der Waal I. The rare sialadenoma papilliferum: report of a case and review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1992;21:104–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
