Comparison between two- and three-dimensional scoring of zebrafish response to psychoactive drugs: identifying when three-dimensional analysis is needed
- PMID: 31637136
- PMCID: PMC6800527
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.7893
Comparison between two- and three-dimensional scoring of zebrafish response to psychoactive drugs: identifying when three-dimensional analysis is needed
Abstract
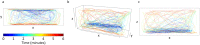
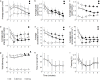
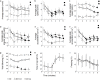
Zebrafish (Danio rerio) have recently emerged as a valuable laboratory species in the field of behavioral pharmacology, where they afford rapid and precise high-throughput drug screening. Although the behavioral repertoire of this species manifests along three-dimensional (3D), most of the efforts in behavioral pharmacology rely on two-dimensional (2D) projections acquired from a single overhead or front camera. We recently showed that, compared to a 3D scoring approach, 2D analyses could lead to inaccurate claims regarding individual and social behavior of drug-free experimental subjects. Here, we examined whether this conclusion extended to the field of behavioral pharmacology by phenotyping adult zebrafish, acutely exposed to citalopram (30, 50, and 100 mg/L) or ethanol (0.25%, 0.50%, and 1.00%), in the novel tank diving test over a 6-min experimental session. We observed that both compounds modulated the time course of general locomotion and anxiety-related profiles, the latter being represented by specific behaviors (erratic movements and freezing) and avoidance of anxiety-eliciting areas of the test tank (top half and distance from the side walls). We observed that 2D projections of 3D trajectories (ground truth data) may introduce a source of unwanted variation in zebrafish behavioral phenotyping. Predictably, both 2D views underestimate absolute levels of general locomotion. Additionally, while data obtained from a camera positioned on top of the experimental tank are similar to those obtained from a 3D reconstruction, 2D front view data yield false negative findings.
Keywords: Anxiety; Automated tracking; Citalopram; Ethanol; Novel tank diving test.
© 2019 Macrì et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Cachat J, Stewart A, Grossman L, Gaikwad S, Kadri F, Chung KM, Wu N, Wong K, Roy S, Suciu C, Goodspeed J, Elegante M, Bartels B, Elkhayat S, Tien D, Tan J, Denmark A, Gilder T, Kyzar E, Dileo J, Frank K, Chang K, Utterback E, Hart P, Kalueff AV. Measuring behavioral and endocrine responses to novelty stress in adult zebrafish. Nature Protocols. 2010;5(11):1786–1799. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2010.140. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

