VWF/ADAMTS13 ratio as a potential biomarker for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 31638892
- PMCID: PMC6802329
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-019-1082-1
VWF/ADAMTS13 ratio as a potential biomarker for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: To investigate the von Willebrand factor to ADAMTS13 ratio as a potential biomarker for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in cirrhosis.
Methods: Serum levels of alpha-fetoprotein, des-γ-carboxy prothrombin, Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein (alpha-fetoprotein-L3%), vascular endothelial growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2, as well as the plasma levels of von Willebrand factor antigen (von Willebrand factor: Ag) and ADAMTS13 activity (ADAMTS13:AC), were evaluated in 41 cirrhotic patients with HCC undergoing radiofrequency ablation and in 20 cirrhotic patients without HCC. The diagnostic accuracy of each biomarker was evaluated using the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis.
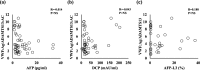
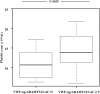
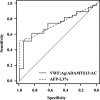
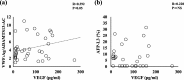
Results: The von Willebrand factor: Ag and von Willebrand factor: Ag/ADAMTS13:AC ratios were significantly higher in cirrhotic patients with HCC than in those without HCC (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively), whereas ADAMTS13:AC was significantly lower in those with HCC than those without HCC (p < 0.05). However, no relationship was observed between the von Willebrand factor: Ag/ADAMTS13:AC ratio and serum tumor markers such as alpha-fetoprotein, des-γ-carboxy prothrombin, and alpha-fetoprotein-L3%. Multivariate regression analysis identified von Willebrand factor: Ag/ADAMTS13:AC ratio and alpha-fetoprotein-L3% as significant factors of HCC development. Receiver operating characteristic analysis showed that the von Willebrand factor: Ag/ADAMTS13:AC ratio and alpha-fetoprotein-L3% had a better performance than alpha-fetoprotein, des-γ-carboxy prothrombin, alpha-fetoprotein-L3%, vascular endothelial growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2, von Willebrand factor: Ag, and ADAMTS13:AC. The von Willebrand factor: Ag/ADAMTS13:AC ratio was exclusively correlated with tumor volume and stage as well as serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels.
Conclusions: The von Willebrand factor: Ag/ADAMTS13:AC ratio can potentially serve as a novel biomarker for early diagnosis of HCC in cirrhotic patients.
Keywords: ADAMTS13; Biomarker; Early diagnosis; HCC; VWF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein: differential diagnosis - hepatocellular carcinoma and other disorders.Clin Liver Dis. 2015 May;19(2):309-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2015.01.005. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Clin Liver Dis. 2015. PMID: 25921665 Review.
-
Combined use of AFP, PIVKA-II, and AFP-L3 as tumor markers enhances diagnostic accuracy for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2016 Mar;51(3):344-53. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2015.1082190. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26340708
-
Clinical Significance of Preoperative Hepatocellular Carcinoma With High Lens culinaris Agglutinin-reactive Fraction of Alpha-Fetoprotein, But Low Alpha-Fetoprotein.Anticancer Res. 2019 Feb;39(2):883-889. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13189. Anticancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30711971
-
A simultaneous monitoring of Lens culinaris agglutinin A-reactive alpha-fetoprotein and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin as an early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in the follow-up of cirrhotic patients.Oncol Rep. 2000 Mar-Apr;7(2):249-56. doi: 10.3892/or.7.2.249. Oncol Rep. 2000. PMID: 10671666
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of alpha-fetoprotein, des-γ-carboxy prothrombin and squamous cell carcinoma antigen immunoglobulin M complexes in hepatocellular carcinoma.Minerva Med. 2011 Oct;102(5):363-71. Minerva Med. 2011. PMID: 22193346 Review.
Cited by
-
ADAMTS13, VWF, and Endotoxin Are Interrelated and Associated with the Severity of Liver Cirrhosis via Hypercoagulability.J Clin Med. 2022 Mar 26;11(7):1835. doi: 10.3390/jcm11071835. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35407443 Free PMC article.
-
Von Willebrand factor in the plasma and in the tumor tissue predicts cancer-associated thrombosis and mortality.Haematologica. 2023 Jan 1;108(1):261-266. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.281315. Haematologica. 2023. PMID: 36134455 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Von Willebrand Factor as a Biomarker for Liver Disease - An Update.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023 Nov-Dec;13(6):1047-1060. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2023.05.016. Epub 2023 Jun 2. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37975050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Locus-specific HERV expression associated with hepatocellular carcinoma.Mob DNA. 2025 Jul 16;16(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13100-025-00367-8. Mob DNA. 2025. PMID: 40671054 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Portal Hypertension in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Systemic Treatment: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 31;16(7):1388. doi: 10.3390/cancers16071388. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kudo M, Hatano E, Ohkawa S, Fujii H, Masumoto A, Furuse J, Wada Y, Ishii H, Obi S, Kaneko S, et al. Ramucirumab as second-line treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Japanese subgroup analysis of the REACH trial. J Gastroenterol. 2017;52(4):494–503. doi: 10.1007/s00535-016-1247-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shima T, Uto H, Ueki K, Kohgo Y, Yasui K, Nakamura N, Nakatou T, Takamura T, Kawata S, Notsumata K, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma as a leading cause of cancer-related deaths in Japanese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. J Gastroenterol. 2018. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

