Gaussian and Mixed Graphical Models as (multi-)omics data analysis tools
- PMID: 31639475
- PMCID: PMC7166149
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.194418
Gaussian and Mixed Graphical Models as (multi-)omics data analysis tools
Abstract
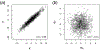
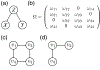
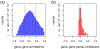
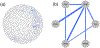
Gaussian Graphical Models (GGMs) are tools to infer dependencies between biological variables. Popular applications are the reconstruction of gene, protein, and metabolite association networks. GGMs are an exploratory research tool that can be useful to discover interesting relations between genes (functional clusters) or to identify therapeutically interesting genes, but do not necessarily infer a network in the mechanistic sense. Although GGMs are well investigated from a theoretical and applied perspective, important extensions are not well known within the biological community. GGMs assume, for instance, multivariate normal distributed data. If this assumption is violated Mixed Graphical Models (MGMs) can be the better choice. In this review, we provide the theoretical foundations of GGMs, present extensions such as MGMs or multi-class GGMs, and illustrate how those methods can provide insight in biological mechanisms. We summarize several applications and present user-friendly estimation software. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Transcriptional Profiles and Regulatory Gene Networks edited by Dr. Dr. Federico Manuel Giorgi and Dr. Shaun Mahony.
Keywords: (Multi-)omics; Gaussian Graphical Model; Gene regulatory network; Mixed Graphical Model.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
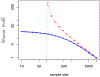

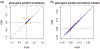

References
-
- Abegaz F and Wit E (2013). Sparse time series chain graphical models for reconstructing genetic networks. Biostatistics, 14(3):586–599. - PubMed
-
- Aldrich J et al. (1995). Correlations genuine and spurious in Pearson and Yule. Statistical science, 10(4):364–376.
-
- Almende B, Thieurmel B, and Robert T (2016). visnetwork: Network visualization using vis.js javascript library. R package version, 1(1).
-
- Altenbuchinger M, Rehberg T, Zacharias H, Stämmler F, Dettmer K, Weber D, Hiergeist A, Gessner A, Holler E, Oefner PJ, et al. (2017a). Reference point insensitive molecular data analysis. Bioinformatics, 33(2):219–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

